UTA research explores how T-cells detect cancer
2023-02-23
A University of Texas at Arlington bioengineering professor is leading a state-funded project that will try to identify what T-cells are detecting in cancerous cells to better craft a personalized cancer immunotherapy.
George Alexandrakis received a $250,000 Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) grant titled “Ultrasensitive Nanosensor-Based Detection of Tumor Immunogenic Peptides to Enable Personalized Cancer Immunotherapy.”
“One of the challenges with cancer is that it is so variable. It changes all the time and is different in all people,” Alexandrakis said. ...
After 25 years of AI health tech research computers are slowly beginning to listen to patients
2023-02-23
Patients experiences of health conditions are slowly being integrated into healthcare AI studies, a review of 25 years of studies has found.
In a new paper published in Lancet Digital Health along with an associated opinion piece, experts from the University of Birmingham and University Hospitals Birmingham have looked at more than 600 interventional studies on AI healthcare technologies.
While the team, funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), found that only 24% of studies have a patient reported outcome element included in their study, there has been an increase in the number in recent years with 2021 and 2022 seeing nearly two thirds of all studies ...
Prioritise tackling toxic emissions from tyres, urge Imperial experts
2023-02-23
Imperial experts are calling for more to be done to limit the potentially harmful impact of toxic tyre particles on health and the environment.
The researchers, from Imperial College London’s Transition to Zero Pollution initiative, warn that even though electric vehicles remove the problem of fuel emissions, we will continue to have a problem with particulate matter because of tyre wear.
Six million tonnes of tyre wear particles are released globally each year, and in London alone, 2.6 million vehicles emit around nine thousand tonnes of tyre wear particles annually.
Despite this, research on the environmental ...
Surge in nitrous oxide abuse: New guidelines to help clinicians recognise cases and prevent spinal cord damage
2023-02-23
Recommendations from research published today on the diagnosis and treatment of spinal cord damage caused by nitrous oxide abuse have been simultaneously adopted as official clinical practice guidelines by the Association of British Neurologists. The unprecedented speed in translating research into practice is necessary as medical cases of nitrous oxide abuse surge in parallel with increased use of what is now the second most popular recreational drug among young people in the UK.
Recreational use of nitrous oxide (N2O - also known as laughing gas) ...
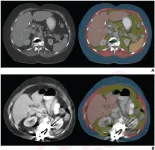
Technical adequacy of artificial intelligence body composition assessed in external CT
2023-02-23
Leesburg, VA, February 23, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), certain reasons for AI tool failure relating to technical factors may be largely preventable through proper acquisition and reconstruction protocols.
“The automated AI body composition tools had high technical adequacy rates in a heterogeneous sample of external CT examinations, supporting the tools’ generalizability and potential for broad use,” concluded head researcher B. Dustin Pooler, MD, from the University of ...
New predatory fish species which lived about 360 million years ago may have grown to over 2.5m long, according to analysis of South African fossils
2023-02-22
New predatory fish species which lived about 360 million years ago may have grown to over 2.5m long, according to analysis of South African fossils
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281333
Article Title: A high latitude Gondwanan species of the Late Devonian tristichopterid Hyneria (Osteichthyes: Sarcopterygii)
Author Countries: South Africa, Sweden
Funding: PEA: Wallenberg Scholarship (not numbered), from the Knut & Alice Wallenberg Foundation. https://kaw.wallenberg.org PEA: ERC Advanced ...
Influence of US weather conditions on tornado trends since 1980 explored by new model
2023-02-22
Influence of US weather conditions on tornado trends since 1980 explored by new model
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281312
Article Title: Long term temporal trends in synoptic-scale weather conditions favoring significant tornado occurrence over the central United States
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Cash transfers in LMICs may help alleviate depression and anxiety symptoms - especially if such transfers are unconditional
2023-02-22
Cash transfers in LMICs may help alleviate depression and anxiety symptoms - especially if such transfers are unconditional
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281283
Article Title: Do cash transfers alleviate common mental disorders in low- and middle-income countries? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Author Countries: UK, Germany
Funding: JS was supported by the Joachim Herz Foundation (https://www.joachim-herz-stiftung.de/en/). AR received funding from the Wellcome Trust (220206/Z/20/Z, ...
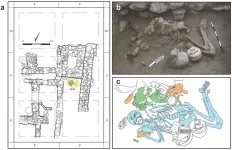
Two high status brothers had access to “brain surgery” in Bronze Age Israel
2023-02-22
Two high status brothers buried in a Bronze Age tomb in Israel were severely ill but apparently had access to rare treatments including trephination, according to a study published February 22, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Rachel Kalisher of Brown University, Rhode Island, and colleagues.
In this study, authors examined the remains of two individuals buried in a tomb beneath an elite residence in the archaeological site of Tel Megiddo in Israel. The tomb dates to the Late Bronze Age (around 1550-1450 BC), and DNA testing suggests the buried individuals are brothers. Both skeletons show evidence of disease, providing an opportunity ...
Archaeologists uncover early evidence of brain surgery in Ancient Near East
2023-02-22
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Archaeologists know that people have practiced cranial trephination, a medical procedure that involves cutting a hole in the skull, for thousands of years. They’ve turned up evidence that ancient civilizations across the globe, from South America to Africa and beyond, performed the surgery.
Now, thanks to a recent excavation at the ancient city of Megiddo, Israel, there’s new evidence that one particular type of trephination dates back to at least the late Bronze Age.
Rachel Kalisher, a Ph.D. candidate at Brown University’s Joukowsky ...
Keeping babies alive will lower population growth – new research
2023-02-22
Keeping babies alive will lower population growth – new research
New research showing high infant mortality rates are contributing to an incessant rise of the global human population supports arguments for greater access to contraception and family planning in low- and middle-income nations.
In an article published in PLOS ONE, research led by Professor Corey Bradshaw, Matthew Flinders Professor of Global Ecology from Flinders University and Peter Le Souëf, Professor of Paediatrics from The University of Western Australia has found that with higher baby death rates and larger household sizes (as an indicator of population density), ...
First transient electronic bandage speeds healing by 30%
2023-02-22
Wireless, battery-free bandage delivers electrical signals to help wounds heal
Bandage monitors healing, streaming data in real time to a smartphone or tablet
After healing is complete, bandage and electronics harmlessly absorb into the body
EVANSTON, Ill. — Northwestern University researchers have developed a first-of-its-kind small, flexible, stretchable bandage that accelerates healing by delivering electrotherapy directly to the wound site.
In an animal study, the new bandage healed ...
Giant proteins in a giant cell: Molecular basis behind fastest biological movement of single-celled eukaryotes
2023-02-22
In his famous letter to the Royal Society dated Oct. 9, 1676, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described a single-celled eukaryote (Vorticella) and its fascinating ultrafast cell contraction as the first set of discoveries. This kind of ultrafast cell contraction triggered by a Ca2+-dependent mechanism is distinct from the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-dependent mechanisms found in actin-myosin and dynein/kinesin-tubulin systems.
Spirostomum, is a genus of millimeter-scale single-celled protists that are known for their incredibly rapid movement like Vorticella. They are capable ...
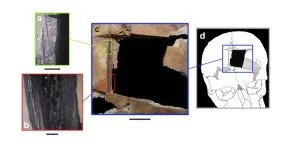
Bow-and-arrow, technology of the first modern humans in Europe 54,000 years ago at Mandrin, France
2023-02-22
If the emergence of mechanically propelled weapons in prehistory is commonly perceived as one of the hallmarks of the advance of modern human populations into the European continent, the existence of archery has always been more difficult to trace. The recognition of these technologies in the European Upper Paleolithic has been hampered by ballistic overlaps between weapons projected with a thruster or a bow. Archery technologies are essentially based on the use of perishable materials; wood, fibers, leather, resins, and sinew, which are rarely preserved in European Paleolithic sites and make archaeological recognition ...
Climate change, urbanization drive major declines in L.A.’s birds
2023-02-22
Berkeley — Climate change isn’t the only threat facing California’s birds. Over the course of the 20th century, urban sprawl and agricultural development have dramatically changed the landscape of the state, forcing many native species to adapt to new and unfamiliar habitats.
In a new study, biologists at the University of California, Berkeley, use current and historical bird surveys to reveal how land use change has amplified — and in some cases mitigated — the impacts of climate ...
Twin-bioengine self-adaptive micro/nanorobots developed for gastrointestinal inflammation therapy
2023-02-22
Micro/nanorobots with self-propelling and -navigating capabilities have attracted extensive attention in drug delivery and therapy owing to their controllable locomotion in hard-to-reach body tissues.
However, developing self-adaptive micro/nanorobots that can adjust their driving mechanisms across multiple biological barriers to reach distant lesions is still a challenge.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. CAI Lintao from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy ...
Custom, 3D-printed heart replicas look and pump just like the real thing
2023-02-22
No two hearts beat alike. The size and shape of the the heart can vary from one person to the next. These differences can be particularly pronounced for people living with heart disease, as their hearts and major vessels work harder to overcome any compromised function.
MIT engineers are hoping to help doctors tailor treatments to patients’ specific heart form and function, with a custom robotic heart. The team has developed a procedure to 3D print a soft and flexible replica of a patient’s heart. They can then ...
Professor Guido Kroemer will inaugurate Redox Medicine 2023 by Highlighting the Hallmarks of Aging & Redox Medicine
2023-02-22
The 25th International Conference on Redox Medicine, on June 21-23 in Paris, will revolutionize tomorrow’s medicine through redox. The translation of basic knowledge of redox into molecular medicine will be extensively discussed.
Prof. Guido Kroemer from the Université de Paris Cité, Hôpital Européen George Pompidou - AP-HP, is the key note speaker for this year. It is a great opportunity to share with Guido Kroemer his favorite topics and to have a unique moment of exchange with him.
Hallmarks of Aging & Redox Medicine: An Expanding Universe
Prof. Kroemer will highlight the “hallmarks of ageing: genomic instability, ...
WVU physicists give the first law of thermodynamics a makeover
2023-02-22
West Virginia University physicists have made a breakthrough on an age-old limitation of the first law of thermodynamics.
Paul Cassak, professor and associate director of the Center for KINETIC Plasma Physics, and graduate research assistant Hasan Barbhuiya, both in the Department of Physics and Astronomy, are studying how energy gets converted in superheated plasmas in space. Their findings, funded by a grant from the National Science Foundation and published in the Physical Review Letters journal, will revamp ...
Yeast used in production of cachaça can prevent asthma, study shows
2023-02-22
A daily dose of a strain of brewer’s yeast used to produce cachaça (distilled spirit made from fermented sugarcane juice) can act as a preventive against asthma, according to a Brazilian study involving male mice. The results are reported in an article published in the journal Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins. The authors are researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) and the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG). The yeast strain used in the study was Saccharomyces cerevisiae UFMG A-905.
Asthma is a common lung condition that causes breathing difficulties. It ...
Out of the blue
2023-02-22
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Blue foods — those that come from the ocean or freshwater environments — have tremendous potential to help address several global challenges. With careful implementation of policies that leverage these foods, nations could get a boost on efforts to reduce nutritional deficits, lower disease risk, decrease greenhouse gas emissions and ensure resilience in the face of climate change.
So say the team of experts at Blue Food Assessment, an international collaboration of scientists whose focus has been on the role of aquatic foods in global ...
Hands-free tech adds realistic sense of touch in extended reality
2023-02-22
HOUSTON – (Feb. 22, 2023) – With an eye toward a not-so-distant future where some people spend most or all of their working hours in extended reality, researchers from Rice University, Baylor College of Medicine and Meta Reality Labs have found a hands-free way to deliver believable tactile experiences in virtual environments.
Users in virtual reality (VR) have typically needed hand-held or hand-worn devices like haptic controllers or gloves to experience tactile sensations of touch. The new “multisensory pseudo-haptic” technology, which is described in an open-access ...
Physically demanding work tied to higher male fertility, study suggests
2023-02-22
A new study from researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, suggests that men who regularly lift heavy objects at work have higher sperm counts. The study, published in Human Reproduction, is part of the Environment and Reproductive Health (EARTH) cohort, a clinical study which aims to explore how exposure to environmental chemicals and lifestyle choices affect reproductive health.
“We already know that exercise is associated with multiple health benefits in humans, including those observed on reproductive health, but few studies have looked at how occupational factors can ...
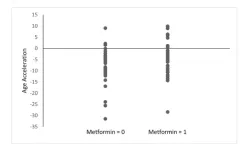
Aging | Metformin's impact on aging and longevity through DNA methylation
2023-02-22
“In this study, we compared genome-wide DNA methylation rates among metformin users and nonusers [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- February 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed as "Aging (Albany NY)" by MEDLINE/PubMed and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 3, entitled, “Metformin use history and genome-wide DNA methylation profile: potential molecular mechanism for aging and longevity.”
Metformin, a commonly prescribed anti-diabetic medication, has repeatedly been shown to hinder aging in pre-clinical ...
As sea ice declines in the Arctic, bowhead whales are adjusting their migration patterns
2023-02-22
NEWPORT, Ore. – As sea ice declines in the Arctic, bowhead whales are staying north of the Bering Strait more frequently, a shift that could affect the long-term health of the bowhead population and impact the Indigenous communities that rely on the whales, a new study by Oregon State University researchers shows.
Bowhead whales found in the Pacific Arctic, sometimes called Bering-Chukchi-Beaufort bowheads based on their migratory patterns, normally winter in the northern Bering Sea and migrate north in the spring through the Bering Strait to the Canadian Beaufort Sea, where they spend summer and fall. They then migrate ...
[1] ... [2096]
[2097]
[2098]
[2099]
[2100]
[2101]
[2102]
[2103]
2104
[2105]
[2106]
[2107]
[2108]
[2109]
[2110]
[2111]
[2112]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.