Excess nutrients lead to dramatic ecosystem changes in Cape Cod’s Waquoit Bay; the bay is a harbinger for estuaries worldwide, say researchers
2023-02-21
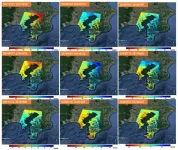
Woods Hole, Mass. (Feb. 21, 2023) -- When the Covid-19 pandemic hit in 2020 with associated travel restrictions, Matthew Long thought his students could shift their overseas research projects to instead study the seagrass meadow ecosystem in Waquoit Bay. It’s a shallow, micro-tidal estuary on the south side of Cape Cod in Massachusetts, near the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) where Long is an associate scientist in the Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Department.
However, when Long and his students looked for seagrass meadows where he had seen them in previous years, there were only a few shoots of dying Zostera marina eelgrass, ...
New AGA guideline recommends blood and stool tests for monitoring ulcerative colitis
2023-02-21
Bethesda, MD (Feb. 21, 2023) — In new evidence-based guidelines, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) recommends non-invasive biomarkers as a first-line strategy for monitoring many patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). These guidelines were published today in Gastroenterology.
The AGA guidelines outline use cases for three biomarkers that provide accurate insights into ulcerative colitis disease activity: serum C-reactive protein (CRP) (blood), fecal calprotectin (stool) and fecal lactoferrin (stool).
“For decades we have regarded endoscopy as the gold ...
RIT researcher awarded NSF CAREER funding to develop advanced computer memory and devices
2023-02-21
Kai Ni was awarded a National Science Foundation CAREER Award to improve computing memory through the use of ferroelectric materials and capacity.
The assistant professor of electrical and microelectronic engineering in RIT’s Kate Gleason College of Engineering, Ni has been at the forefront of advancing ferroelectric memory, a familiar but never widely adopted technology that has the potential to meet the growing demand for more energy-efficient computing performance.
“The appetite for semiconductors just keeps growing. With the data we are generating every day, we need ways to process ...
CHOP researchers develop first effective preclinical models for most common genetic cause of Leigh Syndrome
2023-02-21
Philadelphia, February 21, 2023 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) developed two new zebrafish models for studying a specific genetic form of mitochondrial disease that represents the most common cause of Leigh syndrome. Using these models, the team identified two drugs already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for other conditions that could be repurposed to treat this specific cause of Leigh syndrome. The findings were recently published in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
SURF1 deficiency ...
Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?
2023-02-21
Public lecture: how can we have a good future with artificial intelligence?AI expert and educator Professor Anikó Ekárt to discuss one of today’s most provocative topics
Lecture will take place on 28 February at Aston University
Talk to explore artificial intelligence’s capabilities, benefits and pitfalls.
The potential impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on our daily lives will be explored in a public lecture at Aston University.
The University is inviting the public onto its campus on Tuesday 28 February to hear Professor ...
Study finds parents serve as a safety net as grown kids navigate the workforce
2023-02-21
A new study underscores the role that parents play as a safety net for their young adult children as those children navigate the labor market, and highlights the challenges facing young adults who do not have access to parental support.
“In recent decades, we’ve seen a lot of changes in the labor market, from the decline of lifetime employment at one job to the rise of the so-called ‘gig economy,’” says Anna Manzoni, corresponding author of the study and an associate professor of sociology at North Carolina State University. “We wanted to see what role ...
Noble false widow spider found preying on pygmy shrew
2023-02-21
Scientists at University of Galway have published the first record of a noble false widow spider feeding on a pygmy shrew, a species of tiny mammal protected in Ireland.
The new study, recently published in the international journal Ecosphere, demonstrates further the potentially negative impact of the invasive and venomous noble false widow spider on native species.
A recording by Dawn Sturgess showing the spider interacting with the pygmy shrew be downloaded at https://bit.ly/3XPbDKU.
It is the first time a member of this family of spiders, ...
Starch gelatinization, retrogradation, and the world’s fluffiest white bread (video)
2023-02-21
WASHINGTON, Feb. 21, 2023 — If you want to make the fluffiest bread possible, you’re going to need to use chemistry. This week, we explore the science behind starch gelatinization, a phenomenon found in Chinese “tangzhong” and Japanese “yudane” techniques. Then, we put it to the test to see how much gelatinized starch it takes to make the fluffiest, tastiest and most stale-resistant loaf! https://youtu.be/3ziMBDPMuP8
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to ...
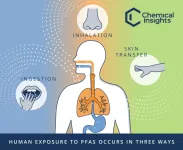
Chemical Insights Research Institute and Emory University’s Rollins School of Public Health team to study the human health impact of PFAS chemical exposure
2023-02-21
ATLANTA – Feb. 21, 2023 – Chemical Insights Research Institute (CIRI) of UL Research Institutes and Emory University's Rollins School of Public Health have announced upcoming research to study human exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that approximately 97% of Americans have detectable PFAS levels in their blood. The joint study aims to understand how this exposure occurs and the potential health consequences.
Although humans may be exposed to PFAS by ingesting food or ...
These sports sensors could curb ‘bad calls’ and help players during practices
2023-02-21
If you watched the most recent Super Bowl, you know the importance of a referee’s call on the outcome of a game. Slow-motion replays and close-watching eyes help, but a new sensor technology could someday serve as an even more reliable tool for officials. Researchers reporting in ACS Applied Nano Materials have developed a self-powered, hybrid nanogenerator sensor that could help make more accurate calls and allow boxers and cricket players to practice more efficiently.
As sensors become less complicated and more ubiquitous, their applications have stretched into the world of sports, ...
Black patients more prone to dialysis graft failure
2023-02-21
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Compared to other races, African American patients are more likely to experience premature arteriovenous (AV) graft failure in the treatment of advanced kidney failure, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Chronic kidney disease affects roughly 37 million U.S. adults, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Over time, chronic kidney disease can result in kidney failure.
One treatment option for advanced kidney failure is hemodialysis, or dialysis, ...
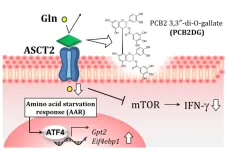
Polyphenols may be missing component in regulating inflammatory immune responses
2023-02-21
PCB2DG, a polyphenol with anti-inflammatory properties, works by targeting and directly interacting with the major glutamine transporter protein, alanine serine cysteine transporter 2 (ASCT2), to inhibit the uptake of glutamine, an important amino acid found in the blood. This reduction of intracellular glutamine accumulation in CD4+ T cells also reduces the production of interferon-gamma, or IFN-γ showing promise in the future of dietary polyphenol treatment for those suffering from autoimmune diseases. Additionally, the identification of ASCT2 as the target protein of PCB2DG is one ...
Study unlocks clues in mystery of naked mole-rats’ exceptional fertility
2023-02-21
Unlike humans and other mammals, which become less fertile with age, naked mole-rats can reproduce throughout their remarkably long lifespans. A new study, published today in Nature Communications, sheds light on unique processes that bestow the rodents with what seems like eternal fertility, findings that could eventually point to new therapies for people.
“Naked mole-rats are the weirdest mammals,” said lead author Miguel Brieño-Enríquez, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor at Magee-Womens Research Institute and the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine’s Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences. “They’re ...
Infants outperform AI in “commonsense psychology”
2023-02-21
Infants outperform artificial intelligence in detecting what motivates other people’s actions, finds a new study by a team of psychology and data science researchers. Its results, which highlight fundamental differences between cognition and computation, point to shortcomings in today’s technologies and where improvements are needed for AI to more fully replicate human behavior.
“Adults and even infants can easily make reliable inferences about what drives other people’s ...
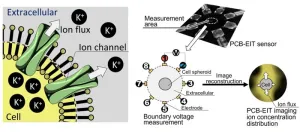
Non-invasive imaging of spatiotemporal ion distribution across cell membranes
2023-02-21
The cell membrane has numerous channels for the transport of various substances, including ions, between the cell and its environment. Ion transport determines the ion exchange rate (or the transmembrane transport coefficient), which, in turn, controls biological functions, such as nerve excitation, heartbeat, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion. It can also be anisotropic, wherein a non-uniform distribution of ions causes different ion exchange rates in different directions. This effect is quite pronounced in heterogeneous tissues. Therefore, the boundaries and overlap of tissues can be detected by measuring the associated anisotropic transmembrane transport.
Fluorescence ...
Investigating land subsidence in Japan through consecutive DInSAR and law of material conservation
2023-02-21
Land subsidence is a phenomenon wherein the Earth’s surface sinks downwards. It occurs mainly due to human activities, such as excessive groundwater extraction. It is a major global concern, affecting 19% of the world’s population. In Japan, some parts of the Tokyo metropolitan region are already sinking. This process can accelerate the flooding of coastal areas and cause damage to buildings and infrastructure. Therefore, monitoring land subsidence is crucial.
In Japan, observation wells are utilized to measure changes in the land surface and groundwater levels every few months. Additionally, the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is also popular. However, ...
Study provides roadmap for using convalescent plasma as an effective COVID-19 treatment
2023-02-21
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Three years into the COVID-19 pandemic, new variant outbreaks continue to fuel economic disruptions and hospitalizations across the globe. Effective therapies remain unavailable in much of the world, and circulating variants have rendered monoclonal antibody treatments ineffective. But a new analysis shows how convalescent plasma can be used as an effective and low-cost treatment both during the COVID-19 pandemic and in the inevitable pandemics of the future.
In a study published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, an international ...
Improving access to reproductive health services among youth with intellectual and developmental disabilities
2023-02-21
New York, NY | February 21, 2023 — The National Institutes of Health (NIH) will award $3,906,026 over five years to researchers from the Institute for Implementation Science in Population Health (ISPH) at the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy (CUNY SPH) to test the efficacy of a new socialization and sex education curriculum for young people with intellectual and developmental disabilities.
CUNY SPH Professor Suzanne McDermott and Associate Professor Heidi Jones will test the curriculum in a randomized controlled trial among 856 adolescents ...
Working a four-day week boosts employee wellbeing while preserving productivity, major six-month trial finds
2023-02-21
Sixty-one organisations in the UK committed to a 20% reduction in working hours for all staff, with no fall in wages, for a six-month period starting in June 2022. The vast majority of companies also retained full-time productivity targets.
Now, results from the world’s largest trial of a four-day working week reveal significantly reduced rates of stress and illness in the workforce – with 71% of employees self-reporting lower levels of “burnout”, and 39% saying they were less ...
Prisons and Probation Ombudsman should improve transparency in death investigations to improve prison safety, report finds
2023-02-21
The UK Prisons and Probation Ombudsman (PPO) must improve transparency when investigating prisoner deaths, according to a new report and policy brief by prison safety experts at the University of Nottingham.
The report, written by Dr Sharon Shalev, draws on research led by Dr Philippa Tomczak in the Faculty of Social Sciences, which offers recommendations to the PPO and policymakers for improving prisoner death investigations and promoting change.
Every year, hundreds of prisoners die in England and Wales — in the 12 months to September 2022, there were 307 deaths in prison custody1. These deaths will almost always be ...
How do parents decide if they should vaccinate their kids against SARS-CoV-2?
2023-02-21
For parents, the decision to vaccinate their kids against SARS-CoV-2 is complex, influenced by scientific evidence, political and social pressures, and views about individual versus collective benefits of vaccination, according to a new study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221401.
Researchers conducted a qualitative study with in-depth interviews of 20 parents to understand their views about SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, with a goal to support future vaccination initiatives.
“Given the ...
Advocacy by LGBTQ+ school clubs may help combat student depression
2023-02-21
Advocacy by student-led Gender-Sexuality Alliance (GSA) clubs could help to reduce school-wide disparities in depressive symptoms between LGBTQ+ and heterosexual students, according to a new study.
The findings, published today in the Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, suggest that schools with GSAs (also known as Gay-Straight Alliances) that engage in more advocacy to highlight issues affecting LGBTQ+ students can help to promote well-being among LGBTQ+ youth across the wider school population.
“Discrimination ...
Does living along the US-Mexico border affect the chances of survival among children with leukemia?
2023-02-21
Residing in border regions was linked with a higher risk of dying within five years among children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the most common type of pediatric cancer.
In an analysis of cancer registry data from Texas, children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who lived along the border with Mexico were more likely to die within five years than those living in other areas of the state. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The ...
New way to predict the damage and aging of bridges by using DNA. technologies
2023-02-21
The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) announced that it has developed the D.N.A. (Data, Network, and AI) technologies to predict the levels of damage and aging of bridges for preventive maintenance.
As of 2021, the percentage of Korean bridges aged 30 years or more stands at a relatively low 12.5%. However, this ratio is expected to increase in the next decade to 39.3% by 2031 and rapidly spike up to 76.1% in 20 years. For the preemptive management of these aging bridges, the ...
Gameto licenses Wyss Institute tech to grow human ovaries in the lab
2023-02-21
Despite the fact that we all start out as an egg cell in one of our mother’s ovaries, these human reproductive organs are surprisingly under-studied. Scientists have been working on creating in vitro models of human ovaries so that we can learn more about them and develop treatments for ovarian conditions, but most existing models use a combination of human and mouse cells, which do not faithfully replicate human ovary functions and take a long time to grow in the lab.
Now, researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University, Harvard Medical School (HMS) and Duke University in collaboration with ...
[1] ... [2101]
[2102]
[2103]
[2104]
[2105]
[2106]
[2107]
[2108]
2109
[2110]
[2111]
[2112]
[2113]
[2114]
[2115]
[2116]
[2117]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.