Take two: Integrating neuronal perspectives for richer results
2021-07-21
Every brain function, from standing up to deciding what to have for dinner, involves neurons interacting. Studies focused on neuronal interactions extend across domains in neuroscience, primarily using the approaches of spike count correlation or dimensionality reduction. Pioneering research from Carnegie Mellon University has identified a way to bridge these approaches, resulting in a richer understanding of neuronal activity.
Neurons use electrical and chemical signals to relay information throughout the body, and we each have billions of them. Understanding how neurons interact with each other is important, ...
Origami comes to life with new shape-changing materials
2021-07-21
Imagine opening up a book of nature photos only to see a kaleidoscope of graceful butterflies flutter out from the page.
Such fanciful storybooks might soon be possible thanks to the work of a team of designers and engineers at CU Boulder's ATLAS Institute. The group is drawing from new advancements in the field of soft robotics to develop shape-changing objects that are paper-thin, fast-moving and almost completely silent.
The researchers' early creations, which they've dubbed "Electriflow," include origami cranes that can bend their necks, flower petals ...
Enamel defects as biomarkers for exposure to environmental stressors
2021-07-21
Alexandria, Va., USA - IADR President Pamela Den Besten presented and chaired the IADR President's Symposium "Enamel Defects as Biomarkers for Exposure to Environmental Stressors" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
Enamel pathologies may result from mutations of genes involved in amelogenesis, or from specific environmental ...
Oral and general health associations using machine learning prediction algorithms
2021-07-21
Alexandria, Va., USA - Muthuthanthrige Cooray, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan, presented the oral session "Oral and General Health Associations Using Machine Learning Prediction Algorithms" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
General health and oral health are conventionally treated as separate entities within the healthcare delivery, however most general health and oral health problems share common ...
The challenge of capturing carbon
2021-07-21
In the race to combat climate change, capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions has been touted as a simple road to reach net-zero emissions by 2050. While the science behind carbon capture is sound, current technologies are expensive and not optimized for all settings. A cover story in Chemical & Engineering News, the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, highlights the current state of carbon capture and work being done to improve the process.
Although efficiency improvements and renewable power sources can help, they are often expensive and will not be enough to counter the billions of tons of CO2 sent into the atmosphere each year, writes Associate ...
Kids eat more fruit and vegetables with longer seated lunch time
2021-07-21
URBANA, Ill. - When kids sit down to eat lunch at school, fruits and vegetables may not be their first choice. But with more time at the lunch table, they are more likely to pick up those healthy foods. If we want to improve children's nutrition and health, ensuring longer school lunch breaks can help achieve those goals, according to research from the University of Illinois.
"Ten minutes of seated lunch time or less is quite common. Scheduled lunch time may be longer, but students have to wait in line to get their food. And sometimes lunch periods are shared with recess. This means the amount of time children actually have to eat their meals is much less than the scheduled time," says ...
Study: Ibrutinib effective treatment for difficult to treat forms of hairy cell leukemia
2021-07-21
COLUMBUS, Ohio - The oral targeted therapy drug ibrutinib is an effective treatment option for high-risk hairy cell leukemia, according to a new study conducted by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center - Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC - James).
Hairy cell leukemia is a rare form of B-cell blood cancer that is diagnosed in 600 to 800 people annually in the United States. Researchers note that while the disease generally has a good prognosis for the majority of people affected, ...
Why weren't New World rabbits domesticated?
2021-07-21
Domesticated rabbits come in all sizes and colors, including tiny Netherland Dwarfs, floppy-eared French lops, Flemish Giants, and fluffy Angoras.
These breeds belong to Europe's only rabbit species, originally limited to the Iberian Peninsula and Southern France and used for meat and fur since the last Ice Age, culminating in domestication about 1,500 years ago.
The Americas, on the other hand, have many rabbit species with ranges throughout both continents. The archaeological record shows rabbits were used as extensively in the Americas as they were on the Iberian Peninsula, with clear archaeological evidence that rabbits were being deliberately raised. Why, then, were rabbits domesticated in Europe and not the Americas?
Recent work ...
Existing drug is shown to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 virus
2021-07-21
A new University of Chicago study has found that the drug masitinib may be effective in treating COVID-19.
The drug, which has undergone several clinical trials for human conditions but has not yet received approval to treat humans, inhibited the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in human cell cultures and in a mouse model, leading to much lower viral loads.
Researchers at UChicago's Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME), working with collaborators at Argonne National Laboratory and around the world, also found that the drug could be effective against many types of coronaviruses and picornaviruses. Because of the way it inhibits replication, it ...
Study links vaccine immune response to age
2021-07-21
Older people appear to have fewer antibodies against the novel coronavirus, a new laboratory study from Oregon Health & Science University suggests.
Antibodies are blood proteins that are made by the immune system to protect against infection. They are known to be key players in protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
"Our older populations are potentially more susceptible to the variants even if they are vaccinated," said senior author Fikadu Tafesse, Ph.D., assistant professor of molecular microbiology and immunology in the OHSU School of Medicine.
Tafesse and colleagues emphasized that even though they measured diminished antibody ...
Policy changes to kidney allocation may unintentionally reduce access to transplant for South Carolina
2021-07-21
The average American spends 5 days each year in line by some estimates. Many of these lines are for things like a cup of coffee, movie theater tickets or a ride on the newest roller coaster, but for some the wait is for something far more pressing -- a new kidney.
In South Carolina, the average time spent on a waitlist for a kidney transplant is 42 months, but according to a recent paper in JAMA Surgery, changes to the U.S. kidney allocation system could result in reduced access to kidney transplants and longer times spent in line.
"At face value, the changes in the allocation system seem quite appropriate," said Derek DuBay, M.D., director of ...
Unexpected proteome plasticity in response to persistent temperature rise
2021-07-21
Common yeast are able to adapt and thrive in response to a long-term rise in temperature by changing the shape, location and function of some of their proteins. The surprising findings demonstrate the unappreciated plasticity in the molecular and conformational level of proteins and bring the power of molecular biology to the organismal response to climate change. Results from the Zhou lab at the Buck Institute in collaboration with the Si lab from the Stowers Institute are published in Molecular Cell.
Temperature is an unstable parameter in the wild, affecting almost ...
The weather forecast for Venus
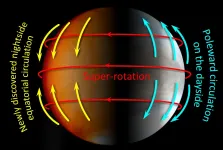
2021-07-21
Little is known about the weather at night on Venus as the absence of sunlight makes imaging difficult. Now, researchers have devised a way to use infrared sensors on board the Venus orbiter Akatsuki to reveal the first details of the nighttime weather of our nearest neighbor. Their analytical methods could be used to study other planets including Mars and gas giants as well. Furthermore, the study of Venusian weather granted by their methods could allow researchers to learn more about the mechanisms underpinning Earth's weather systems.
Earth and Venus ...
Genome editing meets marsupials
2021-07-21
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics Research (BDR) have succeeded in creating the first genetically engineered marsupial. This study, published in the scientific journal Current Biology, will contribute to deciphering the genetic background of unique characteristics observed only in marsupials.
Genetically modified animals, particularly mice and rats, are extremely important tools for researching biological processes. For example, researchers often silence genes to find out what their normal functions are. Since marsupials have unique characteristics, studying them requires developing ...
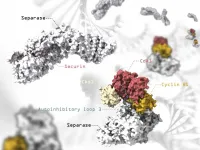
Chromosomes separation under focus
2021-07-21
During cell division, chromosomes are duplicated and separated so that one copy of each chromosome is inherited by each of the two emerging daughter cells. Correct distribution of chromosomes requires high accuracy and defects in this process can cause aberrant distribution of chromosomes and facilitate cancer development. By analyzing the structure of the protein responsible for chromosome separation, an international team, led by scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), has shed light on the mechanisms controlling this essential player in cell division. This work is published in the journal ...
"Magic-angle" trilayer graphene may be a rare, magnet-proof superconductor
2021-07-21
MIT physicists have observed signs of a rare type of superconductivity in a material called magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene. In a study appearing in Nature, the researchers report that the material exhibits superconductivity at surprisingly high magnetic fields of up to 10 Tesla, which is three times higher than what the material is predicted to endure if it were a conventional superconductor.
The results strongly imply that magic-angle trilayer graphene, which was initially discovered by the same group, is a very rare type of superconductor, known as a "spin-triplet," that is impervious to high ...
Association between COVID-19 exposure, self-reported compliance with public health guidelines among essential employees at an institution of higher education
2021-07-21
What The Study Did: This study at an institution of higher education in Colorado evaluated the association between self-reported protective behaviors and how common SARS-CoV-2 infection was among essential in-person employees during the first six months of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States.
Authors: Tracy L. Nelson, M.P.H., Ph.D., of Colorado State University in Fort Collins, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16543)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. ...
Gender-affirming hair removal, mental health outcomes
2021-07-21
What The Study Did: In this analysis of the 2015 U.S. Transgender Survey, gender-affirming hair removal procedures were associated with lower odds of past-month severe psychological distress, past-year smoking and past-year suicidal ideation.
Authors: Michelle S. Lee, B.A., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.2551)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest ...
Preventing approximal caries in primary teeth with topical fluorides
2021-07-21
Alexandria, Va., USA - Parach Sirivichayakul, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand, presented the poster "Preventing Approximal Caries in Primary Teeth With Topical Fluorides" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
There is limited evidence regarding the use of silver diamine fluoride (SDF) for caries prevention in primary teeth. This randomized clinical trial evaluated the effectiveness of 38% SDF, 5% sodium fluoride (NaF) varnish and ...
Researchers discover a 'layer hall effect' in a 2D topological Axion antiferromagnet
2021-07-21
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (7/21/2021) - Researchers have discovered a "layer" Hall effect in a solid state chip constructed of antiferromagnetic manganese bismuth telluride, a finding that signals a much sought-after topological Axion insulating state, the team reports in the current edition of the journal Nature.
Researchers have been trying to find evidence of a topological Axion insulating (TAI) state and developed some candidate materials based on theoretical calculations. The layered Hall effect represents the first clear experimental evidence of the state, a feature bound by the laws of quantum physics, according to Boston College Assistant Professor ...
City-funded housing repairs in low-income neighborhoods associated with drop in crime
2021-07-21
PHILADELPHIA--Investing in structural home repairs in historically segregated, low-income, Black and Latino neighborhoods has been associated with reduced crime rates. In Philadelphia, when a home received repairs through a city-funded program, total crime dropped by 21.9% on that block, and as the number of repaired houses on a block increased, instances of crime fell even further, according to research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania published today in JAMA Network Open.
In an effort to address an old housing stock and high levels of historical disinvestment in Philadelphia, the city implemented the Basic Systems Repair ...
Glass sponges have properties for the design of ships, planes and skyscrapers
2021-07-21
Rome (Italy), July 21st, 2021 - The remarkable structural properties of the basket sponge (E. aspergillum) might seem fathoms removed from human-engineered structures. However, insights into how the organism's latticework of holes and ridges influences the hydrodynamics of seawater in its vicinity could lead to advanced designs for buildings, bridges, marine vehicles and aircraft, and anything that must respond safely to forces imposed by the flow of air or water.
While past research has investigated the structure of the sponge, there have been few studies of the hydrodynamic fields ...
The need for nuance in carbohydrate recommendations
2021-07-21
Carbohydrates have traditionally been the largest source of energy intake for much of the world's population1. However, without a standard definition for carbohydrate quality, some foods that contain carbohydrates are often stigmatized based on isolated and reductionist assessment methods that fail to consider their contributions to nutrient intakes and balanced, healthy diets. A new perspective piece, published in Advances in Nutrition, brings to light the pressing need to define carbohydrate quality, to better assess the value of nutrient-dense carbohydrate-containing foods in healthy lifestyles. Ultimately, the authors call for a more holistic approach to carbohydrate guidance to address the complex ...
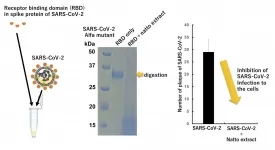
Traditional Japanese food may hold building blocks of COVID-19 treatments
2021-07-21
Natto, a fermented soybean dish often served for breakfast in Japan, originated at the turn of the last millennium but may hold an answer to a modern problem: COVID-19, according to a new study based on cell cultures.
Long thought to contribute to longer, healthier lives across Japan -- the country with the longest life expectancy on Earth and home to more than a quarter of the world's population aged 65 years or older -- natto was previously found to be a diet staple in those who were least likely to die from stroke or cardiac disease. Now, researchers have found that extract made from the sticky, strong smelling natto may inhibit the ability of the virus that causes COVID-19 to infect cells.
The team published its results on July 13th in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. ...
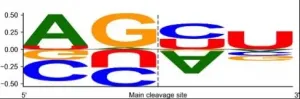
Researchers discover nucleotide sequence responsible for effectively fighting pathologies
2021-07-21
Researchers from HSE University have discovered nucleotide sequences characteristic of microRNA isoforms (microRNAs with errors). The discovery will help predict errors in microRNA behaviour and create drugs that can detect targets (such as viruses) more effectively. The results of the study have been published in the RNA Biology journal.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are very small molecules that regulate all the processes in a cell, including the transformation of inherited information in RNA or proteins (gene expression). Each microRNA has its own unique set of targets--genes whose activity it can suppress. Recent studies show that even slight changes in microRNA nucleotide sequences (so-called microRNA isoforms or isomiRs) can completely rebuild numerous targets. This can drastically ...
[1] ... [2094]
[2095]
[2096]
[2097]
[2098]
[2099]
[2100]
[2101]
2102
[2103]
[2104]
[2105]
[2106]
[2107]
[2108]
[2109]
[2110]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.