Novel algorithm proposed for inversion of aerosol optical depth
2023-02-22
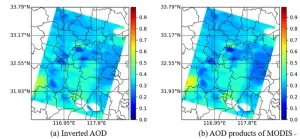
To meet the requirements of single-angle and multi-band polarization aerosol detection, a research team led by Professor SUN Xiaobing from Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed an optimal inversion algorithm based on the combined utilization of multi-band intensity and polarization information.
The result was published in Remote Sensing recently.
Aerosol optical depth (AOD) is used to characterize the extinction effect of aerosol on solar radiation, which plays ...
Therapeutic importance of Ganoderma lucidum highlighted in recent review paper
2023-02-22
According to the research published in Food & Functions recently, a team led by Prof. Huang Qing at the Institute of Intelligent Machines, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), reported for the first time an update and a comprehensive summary of the studies on the immunomodulatory therapies and nutritional significance of Ganoderma lucidum (G. lucidum) from 2010 to 2022, and confirmed that G. lucidum is an essential prebiotic for increasing bacterial flora and a health encouraging agent because of its ...
Alliance for Science and Boyce Thompson Institute launch SciFun Book: A biotechnology program for high school learners
2023-02-22
NAIROBI, KENYA, February 22, 2023 - Alliance for Science (the Alliance) and Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) are excited to launch the SciFun Book, a biotechnology program for high school learners, at the Safari Park Hotel in Nairobi on February 23, 09:00 AM EAT. The SciFun program is designed for Form 2 and Form 3 learners and aims to enhance their understanding of biotechnology through hands-on experience in extracting DNA from fruits and vegetables while making observations about the process.
The curriculum for the SciFun program is a collaborative product of Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO) Science Centre and BTI, and Alliance for Science. Additional ...
A 5-minute PCR, faster than self-diagnosis kits
2023-02-22
PCR technology is a molecular diagnostics technology that detects target nucleic acids by amplifying the DNA amount. It has brought marked progress in the life sciences field since its development in 1984. This technology has recently become familiar to the public due to the COVID-19 pandemic, since PCR can detect nucleic acids that identify the COVID-19 virus. However, due to the technical nature of the PCR test, results cannot be immediately delivered. It takes at least 1 to 2 hours for the test as it requires repeated temperature cycles (60~95℃).
Dr. ...
Nanofluidic devices offer solutions for studying single molecule chemical reactions
2023-02-22
In a chemical reaction, molecules in different substances meet one another to form new molecules causing changes in the bonds of their atoms. The molecules collide at an extremely close distance—a nanometer or less—in an extremely short amount of time. This makes investigating the details of chemical reactions at the molecular scale difficult. Most experimental knowledge, used to explain single-molecule reaction dynamics, was obtained by studying reactions in gases. However, the overwhelming majority of chemical reactions take place in liquids, so elucidating single-molecule reaction dynamics in solution is an important challenge, with very few experimental ...
Keck School of Medicine study finds “forever chemicals” disrupt key biological processes
2023-02-22
A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC found that exposure to a mixture of synthetic chemicals found widely in the environment alters several critical biological processes, including the metabolism of fats and amino acids, in both children and young adults. The disruption of these biological processes is connected to an increased risk of a very broad range of diseases, including developmental disorders, cardiovascular disease, metabolic disease and many types of cancer.
Known as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, these man-made chemicals are used in a wide range of consumer and industrial products. PFAS are sometimes ...
Public voting now open for the 2023 Morgridge Ethics Cartooning Competition
2023-02-21
Eighteen cartoons have been selected as finalists in the 2023 Ethics Cartooning Competition, an annual contest sponsored by the Morgridge Institute for Research.
Participants from the University of Wisconsin-Madison and affiliated biomedical centers or institutes submitted their work, then a panel of judges selected the final cartoons for display to the public, who is invited to vote and help determine the 2023 winners.
This year’s cartoons depict a variety of research ethics topics, such as the ethics of scientific publishing, research funding and environments, questionable research practices, ...
BTI promotes faculty member Fay-Wei Li
2023-02-21
The Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) is delighted to announce that faculty member Fay-Wei Li has been promoted to Associate Professor on January 13. Li was evaluated on his achievements to date and likelihood of continued success in the future.
Since joining BTI in 2017, Li has developed an internationally-recognized program on seed-free plants, both in terms of genome sequencing and in making biological discoveries. He also is an excellent science communicator, with a knack for explaining the importance of scientific discoveries to a wide range of audiences.
The ...
Digital content could be altering your visual perception, new research shows
2023-02-21
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. – So much of modern life is spent on screens: Zoom meetings and websites, smartphones and videogames, televisions and social media. How are all those pixels and rectangles affecting how we see?
Binghamton University, State University of New York Professor of Psychology Peter Gerhardstein and doctoral candidate Nicholas Duggan explore the phenomenon in “Levels of Orientation Bias Differ Across Digital Content Categories: Implications for Visual Perception,” recently published in the journal Perception. Their paper covers the extent to which online content ...
NIH awards researchers $3.14 million grant to design novel model aimed at reducing healthcare disparities
2023-02-21
CLEVELAND: Supported by a new $3.14 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to Cleveland Clinic, researchers are using an emerging technology known as “digital twins” to better understand healthcare disparities based on where someone lives. Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and MetroHealth aim to use this information to develop strategies designed to reduce these disparities in health outcomes.
The research team, led by Jarrod Dalton, Ph.D., of Cleveland Clinic, and Adam Perzynski, Ph.D., of MetroHealth, ...
Study: Whole genome sequencing provides unprecedented detail on the genetic evolution of Hodgkin lymphoma
2023-02-21
(MIAMI, FL, FEB. 21, 2023) – To create the most effective, personalized treatment plans for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma or other cancers, scientists and clinicians need the clearest picture of the genetic changes leading to the cancer’s development. That picture, say scientists at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center in the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, comes into much better focus when whole genome sequencing – rather than the current standard, exome sequencing – is used to identify changes driving the cancer.
Exome sequencing, which reads only protein-coding genes, can detect some specific mutations and other variants that propel cancers, ...
Texas A&M meat scientist developing ‘no nitrite-added’ cured meats
2023-02-21
Written by Kay Ledbetter, 806-547-0002, skledbetter@ag.tamu.edu
Imagine your favorite cured meat like beef jerky, pepperoni or bacon without any added sodium nitrite from any source currently necessary for color and shelf life. Wes Osburn, Ph.D., is doing exactly that.
At center, Wes Osburn, Ph.D., Texas A&M University meat scientist, is working in his lab with students Tanner Wright and Arlie Reeves on a new no nitrite-added cured meat system. (Texas A&M AgriLife photo ...
Conifer-killing beetles use smell of beneficial fungus to select host trees
2023-02-21
Eurasian spruce bark beetles (Ips typographus) burrow into the bark of Norway spruce (Picea abies) trees where they mate and lay their eggs. Major outbreaks in Europe have decimated millions of hectares of conifer forests. The beetles preferentially attack trees that are already infected with symbiotic fungi (such as Grosmannia penicillata), which is thought to weaken host trees and break down their chemical defenses, allowing the beetles to successfully develop in the bark.
To investigate the chemical signals ...
Symbiotic fungi transform terpenes from spruce resin into attractants for bark beetles
2023-02-21
The mass outbreaks of bark beetles observed in recent years have caused shocking amounts of forest damage throughout Germany. As reported by the Federal Statistical Office in July 2022, more than 80% of the trees that had to be felled in the previous year were damaged by insects. The damaged timber felled due to insect damage amounted to more than 40 million cubic meters. One of the main pests is the European spruce beetle Ips typographus. In the Thuringian Forest and the Harz Mountains, for example, the beetle, which is only a few millimeters long, encountered spruce monocultures that had already been weakened by high temperatures and extended ...
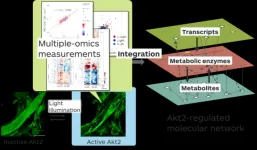
Shining light on an enzyme reveals its role in metabolism
2023-02-21
Takeaki Ozawa and his team from the University of Tokyo reveal the metabolic reactions upon activating an enzyme called Akt2. In doing so, they reveal the inner workings of insulin-regulated metabolism. The findings lead the way for Akt2-targeting therapeutics for diabetes and metabolic disorders.
It takes energy to do anything—even to exist. You can metabolize food to convert glucose into energy: thanks to many cascades of molecular reactions within your cells. As soon as you eat, your pancreas secretes insulin hormone, which starts ...
Impact of key Alzheimer’s protein depends on type of brain cell in which it is produced
2023-02-21
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—February 21, 2023—Of all the known genetic risk factors for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease, the strongest is a gene for the protein called ApoE4. People with one copy of this gene are 3.5 times more likely, on average, to develop Alzheimer’s than others, and those with two copies face a 12-fold increased risk. However, exactly how ApoE4 boosts the risk of Alzheimer’s remains unclear.
Multiple types of cells in the brain make ApoE4—some of it is produced by neurons, but other brain cells called glia make it in higher quantities. For that reason, most prior research on this protein has focused on ...
Douglas Rhoads named AAAS Fellow
2023-02-21
University Professor Douglas Rhoads has been named a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the journal Science.
As one of only 20 fellows representing the Section on Agriculture, Food & Renewable Resources, Rhoads was chosen by his peers and colleagues for advancing science and its applications in service to society. The organization elected a total of 505 fellows across 24 scientific sections.
Rhoads is director of the Interdisciplinary ...
Pill for skin disease also curbs excessive drinking
2023-02-21
Researchers from Oregon Health & Science University and institutions across the country have identified a pill used to treat a common skin disease as an “incredibly promising” treatment for alcohol use disorder.
The study was recently published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
On average, the people who received the medication, called apremilast, reduced their alcohol intake by more than half — from five drinks per day to two.
“I’ve never seen anything like that before,” said co-senior author Angela Ozburn, Ph.D., associate professor of behavioral neuroscience in the OHSU School of Medicine and a research biologist ...
University of Ottawa physician is first Canadian winner of new award focused on health workforce wellness
2023-02-21
The University of Ottawa's Dr. Mamta Gautam is the first awardee of the AFMC Wellness Award, a new national honour that recognizes an individual in Canada who has shown dedication to the promotion and advancement of the wellness of physicians, medical students, and others.
“I am truly humbled and honoured. Promoting physician wellbeing is an area that I have been passionate about for over 30 years. To have the AFMC create an award to recognize contributions in this area lends further credibility to the importance of this topic,” ...
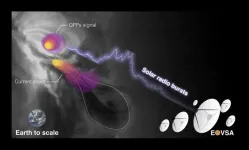
Researchers discover mysterious source of 'heartbeat-like' radio bursts in a solar fare
2023-02-21
A solar radio burst with a signal pattern, akin to that of a heartbeat, has been pinpointed in the Sun’s atmosphere, according to a new study.
In findings published in the journal Nature Communications, an international team of researchers has reported uncovering the source location of a radio signal coming from within a C-class solar flare more than 5,000 kilometers above the Sun’s surface.
Researchers say the study’s findings could help scientists better understand the physical processes behind the energy release of solar flares — the solar system’s most powerful explosions.
“The ...
Three talented researchers recognized as endowed chairs
2023-02-21
Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah (The U) is pleased to congratulate three of our newest endowed chairs. A chair appointment recognizes excellence, while providing academic distinction and funding for future research. Alana Welm, PhD, received a five-year extension in her current role as Ralph E. and Willia T. Main Presidential Endowed Chair in Cancer Research, Aik Choon Tan, PhD, was named the Jon and Karen Huntsman Presidential Professor in Cancer Research, and Brad Cairns, PhD, was named ...
New transmitter design for small satellite constellations improves signal transmission
2023-02-21
Today, there are many emerging applications for small satellite constellations, ranging from space-borne networks to environmental monitoring. However, small satellites have special needs when it comes to transmitter (TX) technology. For one, they have stringent limitations on power consumption as they draw energy from solar panels and cannot easily dissipate generated heat. Moreover, small satellites need to communicate with fast-moving targets that can be over a thousand kilometers away. Thus, they require efficient and precise beam steering capabilities to direct most of the transmitted power ...
Improving the performance of satellites in low Earth orbit
2023-02-21
A database updated in 2022 reported around 4,852 active satellites orbiting the earth. These satellites serve many different purposes in space, from GPS and weather tracking to military reconnaissance and early warning systems. Given the wide array of uses for satellites, especially in low Earth orbit (LEO), researchers are constantly trying to develop better ones. In this regard, small satellites have a lot of potential. They can reduce launch costs and increase the number of satellites in orbit, providing a better network with wider coverage. ...
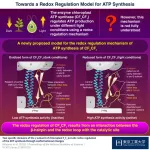
Researchers uncover how photosynthetic organisms regulate and synthesize ATP
2023-02-21
ATP, the compound essential for the functioning of photosynthetic organisms such as plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is produced by an enzyme called “chloroplast ATP synthase” (CFoCF1). To control ATP production under varying light conditions, the enzyme uses a redox regulatory mechanism that modifies the ATP synthesis activity in response to changes in the redox state of cysteine (Cys) residues, which exist as dithiols under reducing (light) conditions, but forms a disulfide bond under oxidizing (dark) conditions. ...
Sheep can benefit urban lawn landscapes and people
2023-02-21
Bicycles whirr by, students rush to class, staff and faculty are grabbing lunch or coffee on the go — and sheep graze the grassy knolls among the traffic, bleating every now and then. The grazing is their job.
The 25 wooly sheep who seasonally — for the past two years — leave their University of California, Davis, barns to nibble on lawns at various central campus locations, are doing much more than mowing, fertilizing and improving the ecosystem. The sheep also are improving people’s mental health.
The sheep — four breeds of Suffolk, Hampshire, Southdown and Dorset — first took on this role in 2021, when COVID-19 ...
[1] ... [2099]
[2100]
[2101]
[2102]
[2103]
[2104]
[2105]
[2106]
2107
[2108]
[2109]
[2110]
[2111]
[2112]
[2113]
[2114]
[2115]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.