Using silicone wristbands to measure air quality
2021-07-23
A study by researchers at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health shows that inexpensive and convenient devices such as silicone wristbands can be used to yield quantitative air quality data, which is particularly appealing for periods of susceptibility such as pregnancy.
The research team found that the wristbands, when used as passive samplers, have the ability to bind smaller molecular weight semi-volatile polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) -- a class of chemicals that occur naturally in coal, crude oil and gasoline and are produced when coal, oil, gas, wood, garbage and tobacco are burned -- in a similar pattern as active sampling.
Published recently in Nature's ...
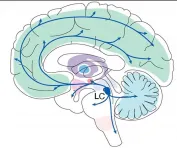
Neuroscientists posit that brain region is a key locus of learning
2021-07-23
Small and seemingly specialized, the brain's locus coeruleus (LC) region has been stereotyped for its outsized export of the arousal-stimulating neuromodulator norepinephrine. In a new paper and with a new grant from the National Institutes of Health, an MIT neuroscience lab is making the case that the LC is not just an alarm button but has a more nuanced and multifaceted impact on learning, behavior and mental health than it has been given credit for.
With inputs from more than 100 other brain regions and sophisticated control of where and when it sends out norepinephrine (NE), the LC's tiny population of surprisingly diverse cells may represent an important regulator of learning from ...
High school student presents on oral-health impact profile 5: analyzing a private practice adult population's distribution
2021-07-23
Alexandria, Va., USA - Hiba Nasir, Wayzata High School, Plymouth, Minn., presented the poster "Oral-Health Impact Profile 5: Analyzing A Private Practice Adult Population's Distribution" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
Nasir, a high school student, along with Sheila Riggs, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA, performed an observational study to understand the ...
Strategies for disseminating guidance to dentists during the COVID-19 pandemic
2021-07-23
Alexandria, Va., USA - Ruth Lipman, American Dental Association (ADA) Science and Research Institute, Chicago, Ill., U.S., presented the poster "Strategies for Disseminating Guidance to Dentists during the COVID-19 Pandemic" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
Rapidly formulated, actionable infection risk mitigation strategies for dental care professionals were needed during the initial acceleration phase of the COVID-19 ...
Policing the digital divide: How racial bias can limit Internet access for people of color
2021-07-23
Coffee shops and casual restaurants are an important part of American life. Even beyond the food and drinks they sell, they offer us a place to use the restroom or rest our feet while we're out and about, and they provide internet access to those on the go, those in need of a temporary office, or those who don't have an internet connection at home. Many of us take for granted that a nearby Starbucks or McDonald's can offer us a little respite, even if we don't always make a purchase.
But access to these sorts of quasi-public spaces isn't always equal in America, particularly for Black people and other people of color. One such example of this is the infamous 2018 incident in Philadelphia when two Black men waiting at Starbucks for an acquaintance were ...
Advantages of intranasal vaccination against SARS-CoV-2
2021-07-23
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - There are many reasons that an intranasal vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus would be helpful in the fight against COVID-19 infections, University of Alabama at Birmingham immunologists Fran Lund, Ph.D., and Troy Randall, Ph.D., write in a viewpoint article in the journal Science.
That route of vaccination gives two additional layers of protection over intramuscular shots because it produces: 1) immunoglobulin A and resident memory B and T cells in the respiratory mucosa that are an effective barrier to infection at those sites, and 2) cross-reactive resident memory B and T cells that can respond earlier than other immune cells if a viral variant does start ...
American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology discusses updated American Cancer Society guidelines on cervical cancer screening
2021-07-23
July 23, 2021 - Last year, the American Cancer Society (ACS) issued an updated set of guidelines for cervical cancer screening - emphasizing the shift toward screening with primary human papillomavirus (HPV) testing. While the ACS recommendation accounts for a transition period to implement primary HPV screening, additional factors should be considered to operationalize these guidelines, according to a special white paper in the July issue of the Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease (JLGTD), official journal of ASCCP. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
In the article, the ASCCP Cervical ...
New tracking system monitors danger to rainforests
2021-07-23
Rainforests are a powerful, natural solution to combat climate change -- providing water filtration, capturing carbon and regulating global temperatures. But major threats like large-scale land use changes, including agricultural expansion and clearcutting, have turned these biodiversity havens into one of the most endangered habitats on our planet.
In 2019, select scientists, including the University of Delaware's Rodrigo Vargas, met at the National Geographic headquarters in Washington, D.C., to discuss the threats to rainforests. The researchers pinpointed a need to develop a worldwide tracking system, which would find trends to help fight land degradation ...
Studies examine different understandings, varieties of diversity
2021-07-23
Attitudes toward diversity vary, and its meaning can often be difficult to find consensus about in an increasingly diverse but politically polarized nation such as the United States.
In a report published by Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, University of Illinois Chicago researchers detail findings from three studies that explore the connection between political ideology, attitudes, and beliefs toward diversity.
"Our studies explored the possibility that atti­tudes toward 'diversity' are multidimensional rather than unidimensional and that ideological differences in diversity attitudes vary as a function of diversity subtype," said the report's ...
Meeting global climate targets will lead to 8 million more energy jobs worldwide by 2050
2021-07-23
Researchers created a global dataset of job footprints in 50 countries and used a model to investigate how trying to meet the Paris Agreement global climate target of staying well below 2°C would affect energy sector jobs. They found that action to reach said target would increase net jobs by about 8 million by 2050, primarily due to gains in the solar and wind industries. The analysis appears July 23 in the journal One Earth.
"Currently, an estimated 18 million people work in the energy industries--a number that is likely to increase, not decrease, to 26 million or by over 50% if we reach our global climate targets," says corresponding author Johannes Emmerling (@JohannesEmm), an environmental economist at the RFF-CMCC ...
New measure of tropical forest vulnerability to help avoid 'tipping point'
2021-07-23
Humid tropical forests, vital in global efforts to limit rising temperatures, are under threat as a result of changes in land use and climate. Now, researchers reporting in the journal One Earth on July 23 have developed a new way to keep tabs on the vulnerability of these forests on a global scale using satellite data. Called the tropical forest vulnerability index (TFVI), the hope is that this method will serve as an early warning for areas that are under the greatest threat to enable actions aimed at protecting these forests before it's too late.
"Frequent droughts, higher temperature, and longer dry seasons, along with increasing pressures from deforestation and ...
US clinics slower to provide opioid treatment than Canadian clinics
2021-07-23
As opioid overdose deaths rose during the COVID-19 pandemic, people seeking treatment for opioid addiction had to wait nearly twice as long to begin methadone treatment in the United States than in Canada, a new Yale study has shown.
In both countries during the pandemic, about one in 10 methadone clinics were not accepting new patients and a third of those cited COVID-19 as the reason, according to research published July 23 in the journal JAMA Network Open.
An estimated 90,000 people in the United States died from drug overdoses last year.
"We missed opportunities to save lives," said Paul Joudrey, assistant professor of internal medicine at the Yale School of Medicine and corresponding author of the paper.
The findings highlight shortcomings providing prompt ...
Americans with higher net worth at midlife tend to live longer
2021-07-23
EVANSTON, Ill., --- One of the keys to a long life may lie in your net worth.
In the first wealth and longevity study to incorporate siblings and twin pair data, researchers from Northwestern University analyzed the midlife net worth of adults (mean age 46.7 years) and their mortality rates 24 years later. They discovered those with greater wealth at midlife tended to live longer.
The researchers used data from the Midlife in the United States (MIDUS) project, a longitudinal study on aging. Using data from the first collection wave in 1994-1996 through a censor date of 2018, the researchers used survival ...
'Feel good' brain messenger can be willfully controlled, new study reveals
2021-07-23
From the thrill of hearing an ice cream truck approaching to the spikes of pleasure while sipping a fine wine, the neurological messenger known as dopamine has been popularly described as the brain's "feel good" chemical related to reward and pleasure.
A ubiquitous neurotransmitter that carries signals between brain cells, dopamine, among its many functions, is involved in multiple aspects of cognitive processing. The chemical messenger has been extensively studied from the perspective of external cues, or "deterministic" signals. Instead, University of California San Diego researchers recently ...
Association of wealth with longevity at midlife
2021-07-23
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated the association between net worth at midlife and subsequent longevity in individuals as well as with siblings and twins.
Authors: Eric D. Finegood, Ph.D., of Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2021.1652)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Experiences, perpetration of identity-based bullying among adolescents
2021-07-23
What The Study Did: Using survey responses from students in some Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, high schools, researchers investigated how experiences of bullying based on race/ethnicity/national origin and other marginalized identities are associated with outcomes for health, mental health and violence among adolescents.
Authors: Chardée A. Galán, Ph.D., of the University of Pittsburgh, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16364)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
Four themes identified as contributors to diseases of despair in Pennsylvania
2021-07-23
Hershey, Pa. -- Financial instability, lack of infrastructure, a deteriorating sense of community and family fragmentation are key contributors to diseases of despair in Pennsylvania communities, according to Penn State College of Medicine and Highmark Health researchers. The researchers conducted four focus groups in Pennsylvania communities identified as having high rates of despair-related illnesses.
Diseases of despair are medical diagnoses involving alcohol-related disorders, substance-related disorders and suicidal thoughts and behavior. Princeton economists Anne Case and Angus Deaton proposed the concept of deaths of despair in 2015 after observing a decline ...
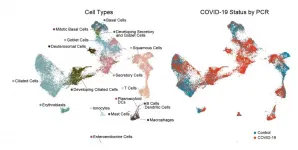
Why do some people get severe COVID-19? The nose may know
2021-07-23
The body's first encounter with SARS-CoV-2, the virus behind COVID-19, happens in the nose and throat, or nasopharynx. A new study in the journal Cell suggests that the first responses in this battleground help determine who will develop severe disease and who will get through with mild or no illness.
Building on work published last year identifying SARS-CoV-2-susceptible cells, a team of collaborators at Boston Children's Hospital, MIT, and the University of Mississippi Medical Center comprehensively mapped SARS-CoV-2 infection in the nasopharynx. They obtained samples from the nasal swabs ...
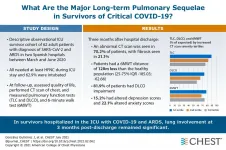
Featured articles from the journal CHEST®, July 2021
2021-07-23
Glenview, Ill. - Published monthly, the journal CHEST® features peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research in chest medicine: Pulmonary, critical care, sleep medicine and related disciplines. Journal topics include asthma, chest infections, COPD, critical care, diffuse lung disease, education and clinical practice, pulmonology and cardiology, sleep, and thoracic oncology.
The July issue of CHEST journal includes 85 articles, clinically relevant research, reviews, case series, commentary and more. Each month, the journal also offers complementary web and multimedia activities, ...
Better healthcare management can reduce the risk of delirium among older adults
2021-07-23
Elderly patients with neurological conditions are significantly more likely to develop delirium shortly after they are hospitalised.
A new study has discovered that a delayed transfer to a hospital floor is associated with greater short-term risk of delirium among patients aged 65 and over, and for those who arrive to the Emergency Department (ED) on days with higher risk of prolonged lengths of stay - found to be Sunday and Tuesday.
Delirium is an acute cognitive disorder characterised by altered awareness, attentional deficits, confusion, and disorientation. Current estimates of new-onset delirium highlight the fact that delirium overwhelmingly develops in medical settings (as high as 82 per cent in intensive care settings) compared ...
Cascaded metasurfaces for dynamic control of THz wavefronts
2021-07-23
Electromagnetic (EM) waves in the terahertz (THz) regime contribute to important applications in communications, security imaging, and bio- and chemical sensing. Such wide applicability has resulted in significant technological progress. However, due to weak interactions between natural materials and THz waves, conventional THz devices are typically bulky and inefficient. Although ultracompact active THz devices do exist, current electronic and photonic approaches to dynamic control have lacked efficiency.
Recently, rapid developments in metasurfaces have opened new possibilities for the creation of high-efficiency, ultracompact THz ...
"Noisy" gene expression may help improve stem cell therapies
2021-07-23
SAN FRANCISCO, CA--July 22, 2021--To speed up a chemical reaction, a chemist might place the reactants over a Bunsen burner. Adding heat increases the degree of random movements and collisions of particles, accelerating the reaction.
In cell biology, one important "reaction" is the transformation of stem cells into all the other cells in the body, a process known as differentiation. Gladstone Institutes researchers have now discovered a molecular mechanism that acts like a Bunsen burner to "turn up the heat" and accelerate differentiation.
However, instead of boosting temperature, this process amplifies random fluctuations ...
Mount Sinai researchers develop novel therapy that could be effective in many cancers
2021-07-23
New York, NY (July 23, 2021) -- Mount Sinai researchers have developed a therapeutic agent that shows high effectiveness in vitro at disrupting a biological pathway that helps cancer survive, according to a paper published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, in July.
The therapy is an engineered molecule, named MS21, that causes the degradation of AKT, an enzyme that is overly active in many cancers. This study laid out evidence that pharmacological degradation of AKT is a viable treatment for cancers with mutations in certain genes.
AKT is a cancer gene that encodes an enzyme that is frequently abnormally activated in cancer cells to stimulate tumor growth. Degradation of ...
New insights into immune responses to malaria
2021-07-23
Advanced technologies have been used to solve a long-standing mystery about why some people develop serious illness when they are infected with the malaria parasite, while others carry the infection asymptomatically.
An international team used mass cytometry - an in-depth way of characterising individual cells - and machine learning to discover 'immune signatures' associated with symptomatic or asymptomatic infections in people infected with the Plasmodium vivax parasite. This uncovered an unexpected role for immune T cells in protection against malaria, ...
How the brain paints the beauty of a landscape
2021-07-23
How does a view of nature gain its gloss of beauty? We know that the sight of beautiful landscapes engages the brain's reward systems. But how does the brain transform visual signals into aesthetic ones? Why do we perceive a mountain vista or passing clouds as beautiful? A research team from the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics has taken up this question and investigated how our brains proceed from merely seeing a landscape to feeling its aesthetic impact.
In their study, the research team presented artistic landscape videos to 24 participants. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), they measured the participants' brain activity as they viewed and rated the videos. Their findings have just been published in the ...
[1] ... [2104]
[2105]
[2106]
[2107]
[2108]
[2109]
[2110]
[2111]
2112
[2113]
[2114]
[2115]
[2116]
[2117]
[2118]
[2119]
[2120]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.