Possible link between late-term births and better academic outcomes, study suggests
2021-07-22
New Brunswick, NJ--Even at term, gestational age may have an impact on children's academic performance, findings of a new study suggest. The research showed an association between gestational age at term and above-average rankings in a number of academic subjects.
The study, published in Pediatrics, compared teacher-reported outcomes for 1,405 9-year-old children in the United States, analyzing performance in mathematics, science and social studies, and language and literacy, for those born at 37 through 41 weeks gestation. It found that longer gestational age was significantly associated with average or above-average rankings in all areas. It also suggested a general pattern of worse outcomes for children born at early term (37-38 weeks) and better outcomes for those born at late ...
Eco-friendly plastic from cellulose and water
2021-07-22
Plastics offer many benefits to society and are widely used in our daily life: they are lightweight, cheap and adaptable. However, the production, processing and disposal of plastics are simply not sustainable, and pose a major global threat to the environment and human health. Eco-friendly processing of reusable and recyclable plastics derived from plant-based raw materials would be an ideal solution. So far, the technological challenges have proved too great. However, researchers at the University of Göttingen have now found a sustainable method - "hydrosetting", which uses water at normal conditions - to process and reshape a new type of hydroplastic polymer called cellulose cinnamate (CCi). The research was published ...
Pathogens get comfy in designer goo
2021-07-22
HOUSTON -- (July 22, 2021) -- Researchers who want bacteria to feel right at home in the laboratory have put out a new welcome mat.
Rice University bioengineers and Baylor College of Medicine scientists looking for a better way to mimic intestinal infections that cause diarrhea and other diseases have built and tested a set of hydrogel-based platforms to see if they could make both transplanted cells and bacteria comfy.
As a mechanical model of intestinal environments, the lab's soft, medium and hard polyethylene glycol (PEG) hydrogels were far more welcoming to the cells that normally line the gut than the glass and plastic usually used by laboratories. These cells can then host bacteria like Escherichia coli that are sometimes pathogenic. The ability to study their ...
What makes a market transaction morally repugnant?
2021-07-22
Many people find it morally impermissible to put kidneys, children, or doctorates on the free market. But what makes a market transaction morally repugnant in the eyes of the public? And which transactions trigger the strongest collective disapproval? Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Human Development and the Robert Koch Institute have addressed these questions. Their findings, published in Cognition, offer new entry points for policy interventions.
Would you be willing to sell a kidney or be paid to spend time on a date? If not, then ...
Gaming graphics card allows faster, more precise control of fusion energy experiments
2021-07-22
Nuclear fusion offers the potential for a safe, clean and abundant energy source.
This process, which also occurs in the sun, involves plasmas, fluids composed of charged particles, being heated to extremely high temperatures so that the atoms fuse together, releasing abundant energy.
One challenge to performing this reaction on Earth is the dynamic nature of plasmas, which must be controlled to reach the required temperatures that allow fusion to happen. Now researchers at the University of Washington have developed a method that harnesses advances in the computer gaming industry: It uses a gaming graphics card, or GPU, to run the control system for their prototype fusion reactor.
The team published ...
Bringing the jury to the crime scene via a 3D headset
2021-07-22
As any juror will tell you, piecing together a crime from a series of documents tendered in a courtroom is no easy feat, especially when a person's future hangs in the balance.
Delivering the correct verdict on car accident and murder cases is contingent on good spatial awareness, but short of being at the scene of the crime, the room for error is large.
However, thanks to the advent of virtual reality (VR), jurors now have a better chance of making the right decision.
A new study published by the University of South Australia provides overwhelming evidence ...
Archaeology: Roman road discovered in the Venice lagoon
2021-07-22
The discovery of a Roman road submerged in the Venice Lagoon is reported in Scientific Reports this week. The findings suggest that extensive settlements may have been present in the Venice Lagoon centuries before the founding of Venice began in the fifth century.
During the Roman era, large areas of the Venice Lagoon which are now submerged were accessible by land. Roman artefacts have been found in lagoon islands and waterways, but the extent of human occupation of the lagoon during Roman times has been unclear.
Mapping the lagoon floor using sonar, Fantina Madricardo and colleagues discovered 12 archaeological structures aligned in a northeasterly direction for 1,140 metres, in an area of the lagoon ...
Palaeontology: Newly-hatched pterosaurs may have been able to fly
2021-07-22
Newly-hatched pterosaurs may have been able to fly but their flying abilities may have been different from adult pterosaurs, according to a study published in Scientific Reports.
Pterosaurs were a group of flying reptiles that lived during the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods (228 to 66 million years ago). Due to the rarity of fossilised pterosaur eggs and embryos, and difficulties distinguishing between hatchlings and small adults, it has been unclear whether newly-hatched pterosaurs were able to fly.
Darren Naish and colleagues modelled hatchling flying abilities using previously obtained wing measurements from four established hatchling and embryo fossils from two pterosaur species, ...
Gene therapy may preserve vision in retinal disease and serious retinal injury
2021-07-22
Gene therapy in mouse models showed promise in preventing vision loss or blindness from serious retinal injury including optic nerve damage, and from retinal disease including diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma, Mount Sinai researchers report. Their study, published in the July 22 online publication of Cell, could transform treatment for those at risk of major vision loss from retinal degenerative diseases, which currently have no cure.
The researchers focused on retinal ganglion cells, which process visual information by sending images to the brain. These cells can degenerate as a result of retinal injury and retinal disease. ...
Geneticists reveal how mutation causes childhood cancer; use drug to reverse its effects
2021-07-22
Geneticists from Trinity College Dublin have discovered how a specific genetic mutation called H3K27M causes a devastating, incurable childhood cancer, known as diffuse midline glioma (DMG), and - in lab studies working with model cell types - successfully reverse its effects to slow cancer cell growth with a targeted drug.
Their landmark work - just published in leading international journal, Nature Genetics and supported by Worldwide Cancer Research and The Brain Tumour Charity - translates crucial new understanding of the genetics of DMG progression into ...
Scientists discover gene therapy provides neuroprotection to prevent glaucoma vision loss
2021-07-22
A form of gene therapy protects optic nerve cells and preserves vision in mouse models of glaucoma, according to research supported by NIH's National Eye Institute. The findings suggest a way forward for developing neuroprotective therapies for glaucoma, a leading cause of visual impairment and blindness. The report was published in Cell.
Glaucoma results from irreversible neurodegeneration of the optic nerve, the bundle of axons from retinal ganglion cells that transmits signals from the eye to the brain to produce vision. Available therapies slow vision loss by lowering elevated eye pressure, however some glaucoma progresses to blindness despite normal eye pressure. Neuroprotective therapies would be a leap forward, meeting ...
Untwisting DNA reveals new force that shapes genomes
2021-07-22
Advances in microscopy have enabled researchers to picture loops of DNA strands for the first time. The images reveal how the human genome organises itself in three-dimensional space at much higher resolution than previously possible.
The findings, published in a new study in the journal Molecular Cell, also reveal that the process of DNA being copied into RNA - transcription - indirectly shapes the architecture of the genome. An international team led by Pia Cosma at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona and Melike Lakadamyali at the Perelman ...
RNA breakthrough creates crops that can grow 50% more potatoes, rice
2021-07-22
Manipulating RNA can allow plants to yield dramatically more crops, as well as increasing drought tolerance, announced a group of scientists from the University of Chicago, Peking University and Guizhou University.
In initial tests, adding a gene encoding for a protein called FTO to both rice and potato plants increased their yield by 50% in field tests. The plants grew significantly larger, produced longer root systems and were better able to tolerate drought stress. Analysis also showed that the plants had increased their rate of photosynthesis.
"The change really is dramatic," said University of Chicago Prof. Chuan He, who together with Prof. Guifang Jia at Peking University, led ...
Wearable devices can reduce collision risk in blind and visually impaired people
2021-07-22
A new study showed that a wearable computer vision device can reduce collisions for both people who are blind or those who are visually impaired and using a long cane and/or guide dog by 37 percent, compared to using other mobility aids alone.
People who have visual impairments are at a significantly higher risk for collisions and falls. Commonly used mobility aids like long canes and guide dogs can offer benefits, but come with limitations in effectiveness and costs, respectively. While some electronic devices are marketed direct-to-consumer claiming to warn wearers of surrounding objects, there has been little evidence of their effectiveness in actual daily mobility settings. This is one of the first randomized-controlled trials to look at the potential benefit of the ...
Prostate cancer treatment among black, white patients during pandemic
2021-07-22
What The Study Did: This study included 647 patients with untreated nonmetastatic prostate cancer (269 patients during the pandemic and 378 from before the pandemic). During the initial COVID-19 lockdown, only 1% of Black men underwent prostatectomy, while 26% of white patients did. Prior to the pandemic, there was no difference in the rate of prostatectomy between the two races (18% of Black men and 19% of white men). The lessons from this study suggest systemic inequities within health care and are likely applicable across medical specialties. Public health efforts are needed to fully recognize the unintended consequence of diversion of cancer resources to the COVID-19 pandemic to develop balanced mitigation strategies as viral rates continue to fluctuate.
Authors: ...
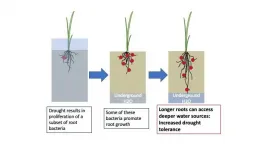
Drought changes rice root microbiome
2021-07-22
Drought can have a lasting impact on the community of microbes that live in and around roots of rice plants, a team led by UC Davis researchers has found. Root-associated microbes help plants take up nutrients from the soil, so the finding could help in understanding how rice responds to dry spells and how it can be made more resilient to drought. The work is published July 22 in Nature Plants.
The root microbiome of irrigated rice plants goes through a sequence of changes as the plants grow and stabilizes when they flower. The sequence of changes in the root ...
Land repair vital for survival
2021-07-22
Restoration of degraded drylands is urgently needed to mitigate climate change, reverse desertification and secure livelihoods for the two billion people who live there, experts warn in a major new paper in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
Scientists leading the Global Arid Zone Project examined restoration seeding outcomes at 174 sites on six continents, encompassing 594,065 observations of 671 plant species - with the lessons learned important to meeting ambitious future restoration targets.
Flinders University Dr Martin Breed, one of three Australian researchers who helped coordinate ...
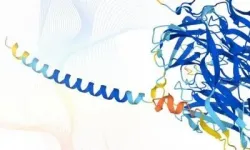
DeepMind and EMBL release the most complete database of predicted 3D structures of human proteins
2021-07-22
LONDON, 22 July 2021 - DeepMind today announced its partnership with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), Europe's flagship laboratory for the life sciences, to make the most complete and accurate database yet of predicted protein structure models for the human proteome. This will cover all ~20,000 proteins expressed by the human genome, and the data will be freely and openly available to the scientific community. The database and artificial intelligence system provide structural biologists with powerful new tools for examining a protein's three-dimensional structure, and offer a treasure trove of data that could unlock future advances and herald a new era for AI-enabled biology.
AlphaFold's recognition in December 2020 by the ...
Newly-hatched pterosaurs may have been able to fly
2021-07-22
Newly-hatched pterosaurs may have been able to fly but their flying abilities may have been different from adult pterosaurs, according to a new study.
Pterosaurs were a group of flying reptiles that lived during the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods (228 to 66 million years ago). Due to the rarity of fossilised pterosaur eggs and embryos, and difficulties distinguishing between hatchlings and small adults, it has been unclear whether newly-hatched pterosaurs were able to fly.
Researchers from the Universities of Portsmouth and Bristol, along with palaeontologist Darren Naish, found that hatchling humerus bones were stronger than those of many adult pterosaurs, indicating ...
A rock with many perspectives
2021-07-22
The Alum Shale of Northern Europe not only has an eventful history of formation, connected with the microcontinent Baltica, it also holds great potential as an object of investigation for future research questions. Geologists use the rock to reconstruct processes of oil and gas formation, and even possible traces of past life on Mars can be identified with its help. Researchers at the German Research Centre for Geosciences Potsdam GFZ, together with colleagues from Canada, China, Switzerland and Denmark, have summarised the state of knowledge about the multi-layered rock. Their article was published in July in the journal Earth-Science Reviews.
The Microcontinent Baltica
"This rock tells a story," says Hans-Martin Schulz when he talks about the Northern European Alum Shale. It is ...
New study reveals previously unseen star formation in milky way
2021-07-22
Astronomers using two of the world's most powerful radio telescopes have made a detailed and sensitive survey of a large segment of our home galaxy -- the Milky Way -- detecting previously unseen tracers of massive star formation, a process that dominates galactic ecosystems. The scientists combined the capabilities of the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) and the 100-meter Effelsberg Telescope in Germany to produce high-quality data that will serve researchers for years to come.
Stars with more than about ten times the mass of our Sun are important components of the Galaxy ...
New insight on the reproductive evolution of land plants
2021-07-22
Around 470 million years ago, plants began to conquer the terrestrial surfaces. The first examples had a small axis terminated by a structure capable of forming spores, almost like current mosses. The appearance of plant organs mediated the explosive radiation of land plants, which shaped the surface of our planet and allowed the establishment of terrestrial animal life.
However, evolving such a diversity of organs, such as roots, leaves, or immobile gametes, requires coordinated genetic changes: rise of new genes, repurpose of genetic material, and development of new regulatory programs. In a study published in Nature Plants, a consortium ...
Unlocking genetic clues behind aortic aneurysm
2021-07-22
A new study increases knowledge of the genetics behind aortic aneurysm, a disease that can spark life-threatening events like aortic dissections and ruptures.
University of Michigan Health-led researchers compared blood samples from more than 1,300 people who had a thoracic aortic aneurysm with more than 18,000 control samples, in partnership with U-M's Cardiovascular Health Improvement Project and its Michigan Genomics Initiative.
"After examining nearly the entire human genome for genetic changes that increase risk of aneurysm, we discovered a new change in the genetic code of a transcription factor, ...
Survival after cardiac arrest - Freiburg cardiovascular surgeons develop new technique
2021-07-22
Around 50,000 people suffer sudden cardiac arrest in Germany every year. When occurring outside a hospital, the chances of survival are only ten percent. Survivors often suffer from severe permanent neurological damage. On July 21st, 2021, researchers from the Faculty of Medicine - University of Freiburg, Germany, published together with German and US colleagues a review article in the journal Nature Reviews Neuroscience. They describe the most important therapeutic factors for successful resuscitation. The scientists name the therapy concept based on these factors ...
Surgeons endorse efforts to improve firearm safety and reduce firearm-related injuries
2021-07-22
Key Takeaways
A survey of American College of Surgeons members found almost two-thirds treat firearm injuries and more than 85 percent support the organization advocating for policies to reduce firearm-related injuries.
Forty-two percent of ACS members keep firearms in their homes and nearly one-third (32 percent) of surgeon firearm owners store firearms unlocked and loaded.
Survey findings will enable the ACS to identify ways to engage all members, including gun owners, and advocate for initiatives that prevent firearm-related injuries.
CHICAGO (July 22, 2021): In what may be the largest survey of physician attitudes about firearms and how firearm-owning surgeons store guns in their homes, U.S. members of the American College of Surgeons ...
[1] ... [2095]
[2096]
[2097]
[2098]
[2099]
[2100]
[2101]
[2102]
2103
[2104]
[2105]
[2106]
[2107]
[2108]
[2109]
[2110]
[2111]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.