Princeton research: Embracing data 'noise' brings Greenland's complex ice melt into focus
2012-11-28
VIDEO:
Princeton University researchers developed an enhanced approach to capturing changes on the Earth's surface via satellite that could provide a more accurate account of how geographic areas change as a...
Click here for more information.
An enhanced approach to capturing changes on the Earth's surface via satellite could provide a more accurate account of how ice sheets, river basins and other geographic areas are changing as a result of natural and human factors. ...
'Fountain of youth' technique rejuvenates aging stem cells
2012-11-28
Toronto, ON (27 November, 2012) -- A new method of growing cardiac tissue is teaching old stem cells new tricks. The discovery, which transforms aged stem cells into cells that function like much younger ones, may one day enable scientists to grow cardiac patches for damaged or diseased hearts from a patient's own stem cells—no matter what age the patient—while avoiding the threat of rejection.
Stem cell therapies involving donated bone marrow stem cells run the risk of patient rejection in a portion of the population, argues Milica Radisic, Canada Research Chair in ...
How vegetables make the meal
2012-11-28
Parents may have some new motivations to serve their kids vegetables. A new Cornell University study, published in Public Health Nutrition, found that by simply serving vegetables with dinner, the main course would taste better and the preparer was perceived to be more thoughtful and attentive.
"Most parents know that vegetables are healthy, yet vegetables are served at only 23% of American dinners," said lead author Brian Wansink, PhD, the John Dyson Professor of Marketing and Consumer Behavior at Cornell University. "If parents knew that adding vegetables to the plate ...
GSA Bulletin: From Titan to Tibet
2012-11-28
Boulder, Colo., USA – GSA Bulletin articles posted online between 2 October and 21 November span locations such as the San Andreas fault, California; Tibet; Mongolia; Maine; the Owyhee River, Oregon; the Afar Rift, Ethiopia; Wyoming; Argentina; the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt; British Columbia; the southern Rocky Mountains; Scandinavia; and Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Topics include the "big crisis" in the history of life on Earth; the structural geology of Mount St. Helens; and the evolution of a piggyback basin.
GSA Bulletin articles published ahead of print are online ...
NASA's TRMM satellite confirms 2010 landslides
2012-11-28
A NASA study using TRMM satellite data revealed that the year 2010 was a particularly bad year for landslides around the world.
A recent NASA study published in the October issue of the Journal of Hydrometeorology compared satellite rain data from NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measurement Mission (TRMM) to landslides in central eastern China, Central America and the Himalayan Arc, three regions with diverse climates and topography where rainfall-triggered landslides are frequent and destructive hazards to the local populations.
The work, led by Dalia Kirschbaum, a research ...
Fast forward to the past: NASA technologists test 'game-changing' data-processing technology
2012-11-28
It's a digital world. Or is it?
NASA technologist Jonathan Pellish isn't convinced. In fact, he believes a computing technology of yesteryear could potentially revolutionize everything from autonomous rendezvous and docking to remotely correcting wavefront errors on large, deployable space telescope mirrors like those to fly on the James Webb Space Telescope.
"It's fast forward to the past," Pellish said, referring to an emerging processing technology developed by a Cambridge, Mass.-based company, Analog Devices Lyric Labs.
So convinced is he of its potential, Pellish ...
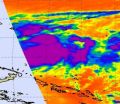
NASA sees Tropical Storm Bopha intensifying in Micronesia
2012-11-28
Tropical storm warnings are in effect in Micronesia as NASA and other satellite imagery indicates that Tropical Storm Bopha continues to intensify.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared image of Tropical Storm Bopha on Nov. 27 at 0241 UTC that indicated a lot of power exists in the strengthening tropical storm. The AIRS image captured the eastern half of the tropical storm and showed a large area of very cold, very high cloud tops, where temperatures colder than -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius) have ...
High altitude climbers at risk for brain bleeds
2012-11-28
CHICAGO – New magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) research shows that mountain climbers who experience a certain type of high altitude sickness have traces of bleeding in the brain years after the initial incident, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
High altitude cerebral edema (HACE) is a severe and often fatal condition that can affect mountain climbers, hikers, skiers and travelers at high altitudes—typically above 7,000 feet, or 2,300 meters.
HACE results from swelling of brain tissue due ...
Most patients in the dark about what radiologists do
2012-11-28
CHICAGO – The role of radiologists in healthcare has long been poorly understood among the general public, but new research presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) shows that even patients who've had imaging exams in the past know little about the profession.
Researchers said the study findings highlight an opportunity for radiologists to educate the public about their role in healthcare.
"We know from previous studies that about half of the general public doesn't even know that radiologists are physicians," said Peter ...
Men with belly fat at risk for osteoporosis
2012-11-28
CHICAGO – Visceral, or deep belly, obesity is a risk factor for bone loss and decreased bone strength in men, according to a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
"It is important for men to be aware that excess belly fat is not only a risk factor for heart disease and diabetes, it is also a risk factor for bone loss," said Miriam Bredella, M.D., radiologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
According to the National Center for Health ...
CT depicts racial differences in coronary artery disease
2012-11-28
CHICAGO – While obesity is considered a cardiovascular risk factor, a study presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) showed that African-American patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) have much less fat around their hearts compared to Caucasian patients.
"Prior evidence suggests that increased fat around the heart may be either an independent marker of CAD burden or a predictor of the future risk of acute coronary events," said U. Joseph Schoepf, M.D., professor of radiology and medicine and director of cardiovascular ...
New study: Many flame retardants in house dust -- unsafe levels
2012-11-28
A peer-reviewed study of the largest number of flame retardants ever tested in homes found that most houses had levels of at least one flame retardant that exceeded a federal health guideline. The journal Environmental Science & Technology will publish the study online on November 28, 12:01am Eastern.
The study led by scientists at Silent Spring Institute tested for 49 flame retardant chemicals in household dust, the main route of exposure for people and especially for children. Forty-four flame retardant chemicals were detected and 36 were found in at least 50% of the ...
Complications challenge rheumatoid arthritis patients after joint replacement surgery
2012-11-28
In the first systemic review of evidence assessing complications following total joint arthroplasty, patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were found to have an increased risk for hip dislocation after hip replacement surgery compared to those with osteoarthritis (OA). Study findings published online in Arthritis & Rheumatism, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), also indicate that RA patients have a higher infection risk following total knee replacement than patients with OA.
The ACR reports that OA—the most common form of arthritis—affects 27 ...
Printing soil science
2012-11-28
Imagine printing a 3-D object as easily as a typed document. Lose a button? Print one. Need a new coffee cup? Print one. While the reality of printing any object on demand may lie in the future, the technology necessary to do it has been available for decades. And soil scientists are now taking advantage of its possibilities.
In a paper published online this week in the Soil Science Society of America Journal, a team of researchers headed by Philippe Baveye explored the potential of manufacturing soil science equipment using 3-D printing. They found that the technology, ...
NREL researchers use imaging technologies to solve puzzle of plant architecture
2012-11-28
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the BioEnergy Science Center (BESC) combined different microscopic imaging methods to gain a greater understanding of the relationships between biomass cell wall structure and enzyme digestibility, a breakthrough that could lead to optimizing sugar yields and lowering the costs of making biofuels.
A paper on the breakthrough, "How Does Plant Cell Wall Nanoscale Architecture Correlate with Enzymatic Digestibility?" appears in the current issue of Science Magazine.
Principal ...
The Threat of Sleepy Drivers in Illinois
2012-11-28
The Threat of Sleepy Drivers in Illinois
Many of us continue to do it even though we know we should not: driving when drowsy. As distracted driving becomes a major road safety concern in Illinois, so too does drowsy driving. Driving tired slows reaction time, decreases awareness and impairs judgment just like drinking and driving and distracted driving. To prevent accidents and to safeguard others on the road, drivers in Illinois should safely pull over when they become too tired to drive.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, sleepy drivers ...
More People Using Technology to Spy on Their Spouse
2012-11-28
More People Using Technology to Spy on Their Spouse
When a couple is struggling in their marriage, tensions and suspicions often run high. As communication between the couple breaks down, some may become concerned and preoccupied with the other's activities. Consequently, as technological advances continue to be made, cases of spouses spying on one another -- either before or during divorceproceedings -- have become more common. Many people fail to realize, though, that such action can violate the law in some states, and occasionally even result in prison sentences.
In ...
Retirement Accounts Play a Unique Role in Your Estate Plan
2012-11-28
Retirement Accounts Play a Unique Role in Your Estate Plan
Retirement is looming large -- or is already here -- for much of the U.S. population. As baby boomers continue to retire and current retirees are living longer, it is clear that retirement accounts must be considered in any estate plan. In fact, as 401(k)s and IRAs become more and more a significant part of retirees' estates, retirement accounts are proving to be the largest asset for many people.
Any good estate plan must account for the tax consequences of retirement accounts. Understanding your retirement ...
Types of Florida Alimony Awards
2012-11-28
Types of Florida alimony awards
Even after a marriage ends, the obligation of one ex-spouse to the other may continue for years, or even a lifetime. Florida courts may grant alimony as a part of marriage dissolution proceedings.
Alimony, which is support paid from one ex-spouse to the other, comes in several different varieties. Some alimony awards are permanent, while others are intended to last only until the person receiving the alimonycan be self-supporting.
Bridge-the-gap alimony
To help transition from married to single life, some ex-spouses receive bridge-the-gap ...
Study Says Your Doctor May Not Always Tell You The Whole Truth
2012-11-28
Study says your doctor may not always tell you the whole truth
The doctor-patient relationship can be a complicated one, as it often occurs at a stressful and busy time for the doctor and the patient. Doctors are human like everyone else and therefore have the same emotions and frailties. Just like in any other human-to-human relationship, there is sometimes a temptation to lie or keep secrets.
A recent survey highlighted the fact that not all doctors believe that being honest and forthright with their patients is the best course of action. The survey, published in ...
Is Pennsylvania's Accelerated Rehabilitative Disposition Right for You?
2012-11-28
Is Pennsylvania's Accelerated Rehabilitative Disposition right for you?
Success can be defined a number of ways in criminal defense cases. Sometimes, an accused person might be completely acquitted of the charges. A more common way to achieve success, however, is to evaluate all of the factors in the case and then work to reach an outcome that minimizes the negative consequences to the accused person.
One of the benefits of working with an experienced criminal defense lawyer is that a lawyer can help an accused person identify and pursue alternative resolution options. ...
Planning ahead and preparing a prenuptial agreement
2012-11-28
Planning ahead and preparing a prenuptial agreement
Prenuptial agreements are often overlooked as useful estate planning and wealth protection documents. The reasons for ignoring these legal needs are not hard to understand, as few people want to contemplate getting a divorce or their own death. Yet rather than being a negative, creating a prenuptial agreement can provide for a family in the event of unexpected life circumstances. A prenuptial agreement can be viewed as a type of insurance policy; much like insurance, a spouse can plan for unforeseen events in the future ...
From Controversial to Party Worthy: The Evolution of Divorce in New York
2012-11-28
From Controversial to Party Worthy: The Evolution of Divorce in New York
Times are changing. Although shows like Mad Men are a hit, viewers are not likely to return to many of the olden values of the fifties and sixties. In fact, Americans are continuing to evolve on how we view social issues that were once controversial. The latest example: Divorce Parties.
According to a recent article in Time Magazine, Divorce Parties are the latest rage trending throughout New York. New York magazine even ran a story discussing how companies throughout the city are specializing ...
A Kansas Doctor's Plea Upheld by Federal Courts
2012-11-28
A Kansas Doctor's Plea Upheld by Federal Courts
Recently, a Kansas doctor pled guilty to a crime and that plea is coming back to haunt him. The doctor is now coming forward to say that that plea was not accurate. A federal judge denied the doctor's claim and upheld the doctor's testimony as proof of his guilt.
The Denial
The doctor had earlier pled guilty to prescribing painkillers in an unlawful manner to a woman that he did not know according to an article in The Republic. When the doctor pled guilty, he stated that he was unaware of the consequences of doing ...
Rocco Leo Gaglioti to Host Heart and Sole
2012-11-28
Rocco Leo Gaglioti Host/Creator of Fashion News Live will be the Host of the Heart and Sole event on December 1, 2012 at Buzz Siler's Gallery in the very hip and fashionable Pearl District of downtown Portland, Oregon.
Gaglioti, Fashion Expert and Celebrity personality, has been involved with many philanthropic causes, including the Miss and Mister Deaf International Pageant held this year in Ankara, Turkey and also, through the United Nations, The Clean Water Initiative Conference held in the Ukraine.
Soles4Souls collects new shoes to give relief to the victims of ...
[1] ... [5580]
[5581]
[5582]
[5583]
[5584]
[5585]
[5586]
[5587]
5588
[5589]
[5590]
[5591]
[5592]
[5593]
[5594]
[5595]
[5596]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.