(Press-News.org) TORONTO, April 24, 2014 – Pregnant immigrants from Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America and Caribbean islands may require increased monitoring during pregnancy, according to new research from St. Michael's Hospital.
The study, published today in the British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, assessed the differences in preeclampsia and eclampsia rates among immigrants and native-born women in six high-immigration countries – Australia (Victoria), Canada (Ontario), Denmark, Sweden, Spain (Catalonia and Valencia) and the United States (California, New Jersey and New York City).
Researchers found that Sub-Saharan Africans have consistently higher risk of preeclampsia and eclampsia compared to immigrants from other world regions or non-immigrant women from the six countries studied. In some, but not all, of the six countries Latin Americans and Caribbean islanders were also shown to be at higher risk.
"Obstetricians and midwives should consider pregnancies for immigrants from these regions as high risk," said Dr. Marcelo Urquia, lead author and an epidemiologist at the Centre for Research on Inner City Health of St. Michael's Hospital. "They need enhanced surveillance and culturally sensitive care."
Preeclampsia is most common in first-time pregnancies. It affects two to seven per cent of women who have never given birth. Mothers with preeclampsia can experience several complications, including high blood pressure and high amounts of protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can cause premature birth and stunt fetus growth in the womb.
If undiagnosed, preeclampsia can lead to eclampsia – a serious condition that puts mothers and children at higher risk. Mothers can suffer long-term cardiovascular health issues. Eclampsia can lead to lost pregnancies and even cause long-term adult health problems in the babies.
"There's no cure for preeclampsia – which does disappear when the baby is born," said Dr. Urquia, who is also an adjunct scientist at the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. "But when caught early, it's easier to manage. That's why it's so important to identify these high-risk groups."
While it's not known why some immigrant groups had higher rates than others, even in their home countries Sub-Saharan Africans exhibit the highest rates of preeclampsia and eclampsia worldwide. It's possible that immigrants may carry higher susceptibility even after arriving in their new country.
Using each country's most recently available birthing data, researchers analyzed more than nine million births – more than a third of which were to immigrant women. Immigrants were divided into regions of origin:
Latin America and the Caribbean islands
Middle East
Western Europe
Eastern Europe
East Asia
Southeast Asia
North Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa
Not all immigrants groups had increased rates of preeclampsia or eclampsia, however. Immigrant women from regions of the world such as East Asia, Southeast Asia, North Africa and the Middle East seem to be at lower risk of developing preeclampsia than native-born women and Eastern Europe women are at lower odds of developing eclampsia.
"It's also important to note that differences exist even within these regional groupings," said Dr. Urquia. "In Ontario, for example, Caribbean and Central American women had greater risk than South Americans– who had similar rates to Canadian-born women."
Western European immigrants acted as a control group for the study -- a population that had endured the immigrant experience but ethnically most resembles those born in the native countries.
"We need to look more at factors affecting immigrant health," said Dr. Urquia. "Future research should continue to look at global evidence."
INFORMATION:
The study was partially funded by a Canadian Institutes of Health Research grant.
About St. Michael's Hospital
St. Michael's Hospital provides compassionate care to all who enter its doors. The hospital also provides outstanding medical education to future health care professionals in 27 academic disciplines. Critical care and trauma, heart disease, neurosurgery, diabetes, cancer care, care of the homeless and global health are among the hospital's recognized areas of expertise. Through the Keenan Research Centre and the Li Ka Shing International Healthcare Education Centre, which make up the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, research and education at St. Michael's Hospital are recognized and make an impact around the world. Founded in 1892, the hospital is fully affiliated with the University of Toronto.
Media contacts
For more information, or to arrange an interview with Dr. Urquia, contact:
Geoff Koehler
Adviser, Media Relations
St. Michael's Hospital
416-864-6060 ext. 6537
koehlerg@smh.ca
Leslie Shepherd
Manager, Media Strategy
St. Michael's Hospital
416-864-6094
shepherdl@smh.ca
Pregnancy complications may be more common in immigrants from certain regions
2014-04-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Moffitt Cancer Center's phase 3 study may be game-changer for acute myeloid leukemia
2014-04-24
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers say clinical trials for a new experimental drug to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are very promising. Patients treated with CPX-351, a combination of the chemotherapeutic drugs cytarabine and daunorubicin, are showing better responses than patients treated with the standard drug formulation.
"Acute myeloid leukemia is an aggressive blood cancer with very low rates of treatment success, especially in older patients," explained Jeffrey Lancet, M.D., senior member of the Department of Malignant Hematology and chief of the Leukemia ...
It's a bubble, but not as we know it
2014-04-24
Multi-sensory technology that creates soap bubbles, which can have images projected onto them or when the bubbles are burst release a scent, will be unveiled at an international conference later this month.
The research paper, to be presented at one of the world's most important conferences on human-computer interfaces - ACM CHI 2014 [26 April-1 May], could be used in areas such as gaming or education and encourage a new way of thinking about multi-sensory technologies.
SensaBubble, led by Professor Sriram Subramanian from the University of Bristol's Department of ...
The Lancet Global Health: Recurrent violence linked to substantially higher rates of mental disorders in post-conflict communities
2014-04-24
In the aftermath of war, communities who continue to experience repeated violence could have a major escalation in rates of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and severe distress, suggests new research published in The Lancet Global Health journal.
In 2004, Dr Derrick Silove from the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia, and colleagues conducted a survey to estimate the prevalence of common mental disorders among 1022 adults (600 from a rural village and 422 from an urban district) in Timor Leste four years after the end of a long-running and violent ...
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology: Vitamin D supplements have little effect on risk of falls in older people
2014-04-24
A new meta-analysis, published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology journal, concludes that there is no evidence to suggest that vitamin D supplements prevent falls, and that ongoing trials to test this theory are unlikely to change this result.
The study, by Dr Mark Bolland of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and colleagues, analysed findings from 20 randomised controlled trials which tested the potential of vitamin D supplements to reduce falls, in a total of 29535 people. The findings show that supplements do not reduce falls by 15% or more, meaning that the ...
Citizen scientists match research tool when counting sharks
2014-04-24
Shark data collected by citizen scientists may be as reliable as data collected using automated tools, according to results published April 23, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Gabriel Vianna from The University of Western Australia and colleagues.
Shark populations are declining globally, and scientists lack data to estimate the conservation status of populations for many shark species. Citizen science may be a useful and cost-effective means to increase knowledge of shark populations on coral reefs, but scientists do not yet know enough about how data collected ...
'Off-the-shelf' equipment used to digitize insects in 3-D
2014-04-24
Scientists have developed a cost-effective, off-the-shelf system to obtain natural-color 3D models of insects, according to results published April 23, 2014, in the open access journal PLOS ONE by Chuong Nguyen from CSIRO in Australia, and colleagues.
Scientists studying insects rely on collected specimens that are often shared between scientists through written descriptions, diagrams, and images. These 2D tools are important in understanding and sharing specimens, but they often lack the precise detail of the actual 3D specimen. The authors of this study, interested in ...
Stem cells in circulating blood affect cardiovascular health, study finds
2014-04-24
COLUMBUS, Ohio – New research suggests that attempts to isolate an elusive adult stem cell from blood to understand and potentially improve cardiovascular health – a task considered possible but very difficult – might not be necessary.
Instead, scientists have found that multiple types of cells with primitive characteristics circulating in the blood appear to provide the same benefits expected from a stem cell, including the endothelial progenitor cell that is the subject of hot pursuit.
"There are people who still dream that the prototypical progenitors for several ...
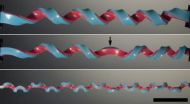
Scientists discover a new shape using rubber bands
2014-04-24
Cambridge, Mass. – April 23, 2014 – While setting out to fabricate new springs to support a cephalopod-inspired imaging project, a group of Harvard researchers stumbled upon a surprising discovery: the hemihelix, a shape rarely seen in nature.
This made the researchers wonder: Were the three-dimensional structures they observed randomly occurring, or are there specific factors that control their formation? The scientists answered that question by performing experiments in which they stretched, joined, and then released rubber strips. Complemented by numerical simulations ...
Microbes provide insights into evolution of human language
2014-04-24
Big brains do not explain why only humans use sophisticated language, according to researchers who have discovered that even a species of pond life communicates by similar methods.
Dr Thom Scott-Phillips of Durham University led research into Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a type of bacteria common in water and soil, which showed that they communicated in a way that was previously thought to be unique to humans and perhaps some other primates.
The bacteria used combinatorial communication, in which two signals are used together to achieve an effect that is different to the ...
People with mild cognitive impairment may die at higher rate than people without condition
2014-04-23
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic research studying the relationship between death and the two types of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) suggests that people who have these conditions die at a higher rate than people without MCI. The research was released today and will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology's 66th Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, April 26 to May 3, 2014.
For the study, 862 people with thinking problems and 1,292 with no thinking problems between the ages of 70 and 89 were followed for nearly six years. Over the course of the study, 331 of the ...