(Press-News.org) TEMPE, Ariz. — During the past few decades, the field of biology has dramatically expanded, incorporating many diverse sub-disciplines and specialty areas such as microbiology and evolutionary biology. However, teaching biology to undergraduate students has not kept pace with the changes, and core biology curriculum varies widely from university to university, and classroom to classroom.
In an effort to both capture the diversity of biology and condense what is taught, an Arizona State University researcher is leading a grassroots effort to improve biology education throughout the United States.
Working with a team from the University of Washington to collect feedback from more than 240 biologists nationwide, ASU assistant professor Sara Brownell has developed a new, detailed core concept template called BioCore Guide. The guide is intended to provide an updated blueprint for educators to help them clarify the learning outcomes for undergraduate students majoring in general biology.
"What we really wanted to articulate was, at the end of four years, what do we want a graduating general biology major to know about the core concepts of biology?" asked Brownell, an education researcher with ASU's School of Life Sciences in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences. "Even if they end up specializing in neuroscience or microbiology, there are some fundamental concepts in ecology and molecular biology that we want them to know. We especially want students to understand that these core concepts extend across sub-disciplines of biology."
The complete guide appears today in the online journal "Cell Biology Education—Life Sciences Education," a quarterly journal frequently read by researchers and biology educators.
BioCore Guide builds on previous reform efforts
Brownell's research builds on initial efforts in 2011 by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the American Association for the Advancement in Science (AAAS) to reform undergraduate biology education. Through conversations with more than 500 biologists and biology educators, NSF and AAAS developed a set of recommendations and five core concepts outlined in the paper "Vision and Change in Undergraduate Biology Education: A Call to Action."
The five core concepts include evolution, information flow, structure function, transformations of energy and matter, and systems.
"Vision and Change provides just a paragraph or two, not a lot of specificity," said Brownell. "It's hard for educators to read, take back to class, and figure out how they should teach a particular subject in biology. So, we decided to more clearly communicate what the core concepts of Vision and Change actually mean for general biology majors. Other sub-disciplines of biology have already done this for students in their sub-discipline specific courses, but no one has done it for general biology majors."
The BioCore Guide provides overarching principles for each core concept, as well as 40 statements that illustrate the concepts within each major subdivision of biology including molecular, cellular and developmental biology; physiology; and ecology and evolutionary biology. The statements and principles have already been nationally validated by hundreds of biologists and biology educators.
Brownell added, "Looking at biology education from a broader perspective, we need to stop lecturing to students in a large lecture hall about the tiny details of biology. One solution is to teach through active learning environments. Another is to start tracking our students' progress through the major."
Brownell and her colleagues plan to use the BioCore Guide as the basis for developing a curriculum assessment that can track how well biology majors understand the core concepts throughout their undergraduate studies. She adds that the BioCore Guide is not meant to dictate when a subject should be taught, or what to teach, but rather to serve as a resource for both faculty and biology departments to generate conversations that lead to a plan for improvements in biology education.
INFORMATION:
University of Washington College of Arts and Sciences, University of Washington Department of Biology, and NSF DUE 1323101 collaborative research grant provided funding for this project.
ASU researcher leads national effort to transform undergraduate biology education
Goal is to clarify learning outcomes for general biology majors
2014-06-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New UGA research engineers microbes for the direct conversion of biomass to fuel
2014-06-02
Athens, Ga. – The promise of affordable transportation fuels from biomass—a sustainable, carbon neutral route to American energy independence—has been left perpetually on hold by the economics of the conversion process. New research from the University of Georgia has overcome this hurdle allowing the direct conversion of switchgrass to fuel.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, documents the direct conversion of biomass to biofuel without pre-treatment, using the engineered bacterium Caldicellulosiruptor bescii.
Pre-treatment ...
Tracking potato famine pathogen to its home may aid $6 billion global fight
2014-06-02
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The cause of potato late blight and the Great Irish Famine of the 1840s has been tracked to a pretty, alpine valley in central Mexico, which is ringed by mountains and now known to be the ancestral home of one of the most costly and deadly plant diseases in human history.
Research published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, by researchers from Oregon State University, the USDA Agricultural Research Service and five other institutions, concludes that Phytophthora infestans originated in this valley and co-evolved with potatoes ...
Tumor size is defining factor to response from promising melanoma drug
2014-06-02
CHICAGO — In examining why some advanced melanoma patients respond so well to the experimental immunotherapy MK-3475, while others have a less robust response, researchers at Mayo Clinic in Florida found that the size of tumors before treatment was the strongest variable.
MULTIMEDIA ALERT: Video and audio are available for download on the Mayo Clinic News Network.
They say their findings, being presented June 2 at the 50th annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), offered several clinical insights that could lead to different treatment strategies ...
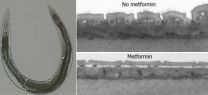
Anti-diabetic drug slows aging and lengthens lifespan
2014-06-02
A study by Belgian doctoral researcher Wouter De Haes (KU Leuven) and colleagues provides new evidence that metformin, the world's most widely used anti-diabetic drug, slows ageing and increases lifespan.
In experiments reported in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers tease out the mechanism behind metformin's age-slowing effects: the drug causes an increase in the number of toxic oxygen molecules released in the cell and this, surprisingly, increases cell robustness and longevity in the long term.
Mitochondria – the energy factories ...
Marijuana shows potential in treating autoimmune disease
2014-06-02
A team of University of South Carolina researchers led by Mitzi Nagarkatti, Prakash Nagarkatti and Xiaoming Yang have discovered a novel pathway through which marijuana can suppress the body's immune functions. Their research has been published online in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Marijuana is the most frequently used illicit drug in the United States, but as more states legalize the drug for medical and even recreational purposes, research studies like this one are discovering new and innovative potential health applications for the federal Schedule I drug. ...
Shape matters...
2014-06-02
Which look bigger, packages of complicated shape or packages of simple shape? Some prior research shows that complex packages appear larger than simple packages of equal volume, while other research has shown the opposite - that simple packages look bigger than the more complex. US researchers, writing in the International Journal of Management Practice believe they have resolved this dilemma.
Lawrence Garber of Elon University in North Carolina and Eva Hyatt and Ünal Boya of Appalachian State University report that human beings are just not very good at estimating the ...
Carnegie Mellon researchers discover social integration improves lung function in elderly
2014-06-02
PITTSBURGH—It is well established that being involved in more social roles, such as being married, having close friends, close family members, and belonging to social and religious groups, leads to better mental and physical health. However, why social integration — the total number of social roles in which a person participates — influences health and longevity has not been clear.
New research led by Carnegie Mellon University shows for the first time that social integration impacts pulmonary function in the elderly. Lung function, which decreases with age, is an important ...
Study suggests fast food cues hurt ability to savor experience
2014-06-02
Toronto – Want to be able to smell the roses?
You might consider buying into a neighbourhood where there are more sit-down restaurants than fast-food outlets, suggests a new paper from the University of Toronto's Rotman School of Management.
The paper looks at how exposure to fast food can push us to be more impatient and that this can undermine our ability to smell the preverbal roses.
One study, surveyed a few hundred respondents throughout the US on their ability to savor a variety of realistic, enjoyable experiences such as discovering a beautiful waterfall on ...
Gene therapy combined with IMRT found to reduce recurrence for select prostate cancer patients
2014-06-02
Fairfax, Va., June 2, 2014—Combining oncolytic adenovirus-mediated cytotoxic gene therapy (OAMCGT) with intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) reduces the risk of having a positive prostate biopsy two years after treatment in intermediate-risk prostate cancer without affecting patients' quality of life, according to a study published in the June 1, 2014 edition of the International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (Red Journal), the official scientific journal of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO).
Previous prospective ...
How Thomas Edison laid the foundation for the modern lab (video)
2014-06-02
WASHINGTON, June 2, 2014 — Thomas Edison is hands-down one of the greatest inventors in history. He also had a love of chemistry that banished him to the basement as a kid. This week, the Reactions team went behind the scenes at the Thomas Edison National Historical Park to see how Edison's love of chemistry fueled his world-changing inventions. Recently named a National Historic Chemical Landmark, the complex is home to more than 400,000 artifacts (which we definitely weren't allowed to touch) and is considered the template for modern research-and-development labs everywhere. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
[Press-News.org] ASU researcher leads national effort to transform undergraduate biology educationGoal is to clarify learning outcomes for general biology majors