Anxiety among fathers is higher than recently reported, new study suggests
A new study explores the prevalence rate of anxiety for fathers during the perinatal period
2021-04-05
(Press-News.org) New research suggests anxiety among men transitioning into parenthood is significantly higher than reported by the global World Health Organization (WHO) regional prevalence rates.
In a new study published in The Journal of Psychosomatic Obstetrics & Gynecology, researchers from the Colorado School of Public Health on the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus studied the prevalence of anxiety among fathers during the perinatal period, which includes pregnancy through the first year of postpartum.
"The transition to parenthood is a major life event that's often accompanied with new challenges related to financial, relationship, and work-life balance concerns. Despite those changes happening for both men and women, not much is known about the prevalence of anxiety among new fathers," said Jenn Leiferman, PhD, professor at the Colorado School of Public Health. "To our knowledge, our study is the first meta-analysis to explore the prevalence rates of anxiety among both fathers and mothers during the perinatal period."
The researchers reviewed eligible studies representing more than 40,000 participants that have published between 1995-2020. The researchers found that the overall estimate of anxiety among men during the perinatal period was nearly 11 percent, with rates being lower during pregnancy (9.9 percent) than during the first year postpartum (11.7 percent).
These rates are considerably higher than the global WHO regional prevalence rates for anxiety among men that range between 2.2 to 3.8 percent, suggesting the transition into parenthood may increase risk for anxiety in men.
In terms of anxiety among mothers, the researchers found an estimated 17.6 percent of women experience it during the perinatal period. This is also substantially higher than global WHO regional preferences for anxiety among women, but in line with estimates for maternal anxiety from other meta-analyses.
"The prevalence of anxiety and depression among men is talked about less as a society, even though research shows men are more likely to commit suicide or abuse alcohol than women. It's important that we create more transparency around men's mental health issues. Our hope is by creating awareness, we can help people get help earlier when needed," said Leiferman.
The researchers suggest that many men suffer anxiety during the transition to parenthood, starting as soon as the first trimester throughout the first year postpartum. Given this, identifying appropriate support for new fathers as well as early identification and treatment efforts for paternal anxiety are needed.
INFORMATION:
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education, and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes, and two nationally ranked independent hospitals that treat more than two million adult and pediatric patients each year. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, together we deliver life-changing treatments, patient care, professional training, and conduct world-renowned research. For more information, visit http://www.cuanschutz.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-05
The diffraction limit, also known as Abbe diffraction limit in optics, poses a great challenge in many systems that involve wave dynamics, such as imaging, astronomy, and photolithography. For example, the best optical microscope only possesses resolution around 200 nm, but the physical size of the photolithography process with an excimer laser is around tens of nanometers. Meanwhile, physical sizes in current research and applications in biology and the semiconductor industry have scaled down to several nanometers, which is far beyond the ability of optical waves. According ...
2021-04-05
A new publication from the Dauphin Island Sea Lab's Marine Mammal Research Program (DISL) examines how bridge-building and in-water construction activities may affect manatees and other large aquatic species. The article, which was recently published in END ...
2021-04-05
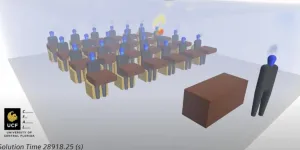
ORLANDO, April 5, 2021 - A new study from the University of Central Florida suggests that masks and a good ventilation system are more important than social distancing for reducing the airborne spread of COVID-19 in classrooms.
The research, published recently in the journal Physics of Fluids, comes at a critical time when schools and universities are considering returning to more in-person classes in the fall.
"The research is important as it provides guidance on how we are understanding safety in indoor environments," says Michael Kinzel, an assistant professor in UCF's Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and study co-author.
"The study finds that aerosol transmission routes do not display ...
2021-04-05
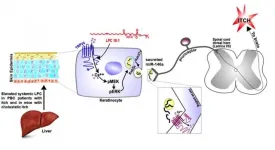
DURHAM, N.C. - A devastating itching of the skin driven by severe liver disease turns out to have a surprising cause. Its discovery points toward possible new therapies for itching, and shows that the outer layer of the skin is so much more than insulation.
The finding, which appears April 2 in Gastroenterology, indicates that the keratinocyte cells of the skin surface are acting as what lead researcher Wolfgang Liedtke, MD PhD, calls 'pre-neurons.'
"The skin cells themselves are sensory under certain conditions, specifically the outermost layer of cells, the keratinocytes," said Liedtke, who is a professor of neurology ...
2021-04-05
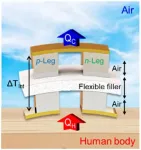
Despite the continued development and commercialization of various wearable electronic devices, such as smart bands, progress with these devices has been curbed by one major limitation, as they regularly need to be recharged. However, a new technology developed by a South Korean research team has become a hot topic, as it shows significant potential to overcome this limitation for wearable electronic devices.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), or KIST, announced that a research team led by Director Jin-Sang Kim of the Jeonbuk Institute of Advanced Composite ...
2021-04-05
A new study at Tel Aviv University reveals a possible defense mechanism developed by fireflies for protection against bats that might prey on them. According to the study, fireflies produce strong ultrasonic sounds - soundwaves that the human ear, and more importantly the fireflies themselves, cannot detect. The researchers hypothesize that these sounds are meant for the ears of bats, keeping them away from the poisonous fireflies, and thereby serving as a kind of 'musical armor'. The study was led by Prof. Yossi Yovel, Head of the Sagol School of Neuroscience, and a member of the School of Mechanical Engineering and the School of Zoology at the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences. It was conducted in collaboration with the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST). ...
2021-04-05
Could the next Hollywood blockbuster be written by a computer? Scientists from the University of Granada (UGR) and the University of Cádiz (UCA) have designed the world's first computer system based on artificial intelligence techniques that can help film scriptwriters create storylines with the best chance of box-office success.
The researchers focused their analysis on the "tropes" of existing films--that is, the commonplace, predictable, and even necessary clichés that repeatedly feature in film plots, based on rhetorical figures. These storytelling devices and conventions enable directors to readily convey scenarios that ...
2021-04-05
A lot of people think regret must be a good thing because it helps you not repeat a mistake, right?
But that turns out not to be the case. Not even when it comes to casual sex, according to new research from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Psychology.
"For the most part, people continue with the same sexual behaviour and the same level of regret," says Professor Leif Edward Ottesen Kennair.
So, we repeat what we thought was a mistake, and we regret it just as much the next time around.
Professor Kennair and colleagues professor Mons Bendixen and postdoctoral ...
2021-04-05
Scientists from Russia and Germany studied the molecular composition of carbonaceous chondrites - the insoluble organic matter of the Murchison and Allende meteorites - in an attempt to identify their origin. Ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry revealed a wide diversity of chemical compositions and unexpected similarities between meteorites from different groups. The research was published in the Scientific Reports.
Carbonaceous chondrites contain nearly the entire spectrum of organic molecules encountered on Earth, including nucleic acids which might have played a pivotal role in the origin of life. Since the majority of modern meteorites are of nearly the same age ...
2021-04-05
WHO Ingrid Katz, MD, MHS, Associate Physician, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; lead author of a new Perspective piece published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
WHAT While the U.S. has begun to vaccinate millions of Americans each day, COVID-19 vaccine supplies around the world remain scarce. Experts estimate that 80 percent of people in low-resource countries will not receive a vaccine in 2021. At the time of the paper's writing, the global vaccination rate was 6.7 million doses per day -- a rate at which it would take 4.6 years to achieve global herd immunity. In a new Perspective piece in the New England Journal of Medicine, Katz and colleagues highlight the need ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Anxiety among fathers is higher than recently reported, new study suggests
A new study explores the prevalence rate of anxiety for fathers during the perinatal period