(Press-News.org) ‘Let us remember the lessons of the coronavirus to usher in a new era on a global scale with different personal and collective behaviour so that everyone, not just a few, enjoys the dignified life that is their due. We have to remember that we cannot go back to “pre-COVID”. We have to keep in mind that the circumstances before the pandemic most likely contributed in some way to the situation as have had to live it. A radical change of course is indispensable and urgent…”
~Federico Mayor Zaragoza, Former Director-General of UNESCO and Former Member of the European Parliament.
Where did COVID-19 originate? Prof Angus Dalgleish shows that the virus that emerged in Wuhan, China in 2019 had been modified in a laboratory to make it more infectious (for the construction of a more effective vaccine). Unfortunately the virus appears to have leaked out of the institute laboratory and so caused some seven million deaths worldwide. Professor Dalgleish’s conclusion has recently been vindicated by others, including science author Matt Ridley and public bodies like the US Senate, Federal Bureau of Investigation, and the US Department of Energy.
A multi-author volume, the chapters in Evaluating a Pandemic
In this book, the COVID-19 outbreak is compared with previous epidemics that have occurred in the past. The aim of this book is to provide a review of the situation from 2020 to 2022, and to consider how to react in future epidemics. Readers will find the contrast between the economic consequences of lockdown in Sweden and the UK particularly illuminating.
This volume begins with the source of the SARS-COV-2 virus, before proceeding to analyse the high-speed development, manufacturing and distribution of ‘classical’ and novel vaccines against COVID-19. It also presents an assessment of the diagnostics used to identify infected patients and prevent the spread of the virus to those at risk of severe disease and death, and how lessons learned from them can help us confront future epidemic and endemic diseases. Evaluating a Pandemic includes scholarly analyses of various countries’ responses to the pandemic and their respective economic and sociological aftermaths, and discusses what we can learn from them.
This publication is a valuable resource for scientists, clinicians, psychologists, economists, bureaucrats, and politicians who deal with or write policies in preparation for future endemic and/or pandemic diseases. Historians and sociologists may benefit from the information collected and presented within.
Evaluating a Pandemic retails for US$78 / £60 (hardcover) and is also available in electronic formats. To order or know more about the book, visit http://www.worldscientific.com/worldscibooks/10.1142/13039.
###
About the Editor
Professor Charles Pasternak is a British biochemist and founding Director of the Oxford International Biomedical Centre, of which he is currently President. He has published over 250 original papers and reviews, and is the founding Editor-in-Chief of Bioscience Reports, helming the journal for 28 years. He is also the editor of Biosciences 2000 (World Scientific, 1999), and author of eight other books.
Educated at Oxford University, Charles Pasternak spent 15 years on the staff of the Oxford Biochemistry Department, during which time he also held a teaching Fellowship at Worcester College, Oxford. He spent two years as a Post-Doctoral Fellow in the Pharmacology Department of Yale University Medical School, and subsequently held an Eleanor Roosevelt Fellowship of the International Union Against Cancer in the Department of Neurosciences at the University of California San Diego Medical School in La Jolla. In 1976 he was invited to move to St. George's Hospital Medical School, University of London, in order to set up a new Department of Biochemistry, which he subsequently expanded into a larger Department of Cellular and Molecular Sciences as founder-Chairman. He is currently President of the Oxford International Biomedical Centre which he founded in 1992.
Charles Pasternak is a tireless promoter of international scientific collaboration. He has been a member of the Executive Committee for a UNESCO initiative on Molecular and Cellular Biology, a member of the Education Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), a member of the International Advisory Board for the Chulabhorn Research Institute, Bangkok and a member of the Scientific Board of Antenna Technologie, Geneva. In 1979 he founded the Cell Surface Research Fund in order to foster international research links and scientific meetings on various aspects of fundamental and clinical research on the cell surface. In 1993 he received the degree of Doctor Honoris Causa and Palade medal from the University of Bucharest, in 1995 the honour of Amigo de Venezuela from the Fundacion Venezuela Positiva, and in 2002 was elected Foreign Member of the Polish Academy of Arts and Sciences.
About World Scientific Publishing Co.
World Scientific Publishing is a leading international independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research and professional communities. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organisations like the Nobel Foundation and US National Academies Press to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. The company publishes about 600 books and over 170 journals in various fields annually. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit www.worldscientific.com.
For more information, contact WSPC Communications at communications@wspc.com.
END
COVID-19: Lessons from the Pandemic
Why Sweden got it right, but most countries did not
2023-09-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
OB/Gyn residency programs should offer more menopause training
2023-09-01
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Sept. 1, 2023) – A nationwide assessment of Obstetrics and Gynecology residency programs reveals the need for more training in how to provide the best care for women going through menopause, according to investigators at the Medical College of Georgia.
“When you look at projections over the next few decades, by 2060, there will be around 90 million women in the US alone, who will be in the post-menopausal range,” says Jennifer Allen, MD, associate professor and director of the Obstetrics and Gynecology Residency Program ...
Deprived teens with poor learning skills at greatest risk from email scams, says expert
2023-09-01
Disadvantaged teenagers are at greater risk of email scams and need better protection, according to an international study published in the peer-reviewed British Journal of Educational Studies.
Findings based on more than 170,000 students aged 15 show that one in five from low-income families or deprived areas could fall victim to phishing. This is much higher than the probability for the age group overall. Email scams leave people vulnerable to identity theft, putting young people at risk of financial fraud and having their savings stripped.
The most vulnerable are those who also have poor learning skills according to the data from 38 countries including ...
Metal organic framework nanosheets employed as ion carriers for self-optimized zinc anode
2023-09-01
Aqueous rechargeable zinc ion batteries are promising in electric grid storage due to their low cost and intrinsic safety. However, their practical implementation is hindered by poor reversibility of the zinc anode, primarily caused by the chaotic Zn deposition present as dendrite and side reactions.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. YANG Weishen and Dr. ZHU Kaiyue from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has proposed a strategy of "ion ...
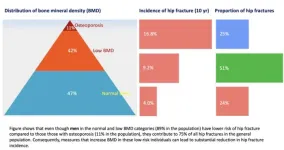
How little things can reduce hip fractures
2023-09-01
Simple strategies to strengthen your bones, implemented by the whole community not just those at higher risk, could lead to a substantial decrease in hip fractures, a new Australian study suggests.
A hip fracture, particularly in the elderly, dramatically increases the risk of death. Around 37 per cent of men and 20 per cent of women die within one year of a hip fracture. It also causes significant pain and suffering, loss of mobility and independence, and increased healthcare costs.
Distinguished Professor Tuan Nguyen, ...
Heart transplant patients from socioeconomically distressed communities face higher mortality, organ failure risk
2023-09-01
FINDINGS
People from socioeconomically distressed communities who underwent heart transplantation between 2004 and 2018 faced a 10% greater relative risk of experiencing graft failure and dying within five years compared to people from non-distressed communities. In addition, following implementation of the 2018 UNOS Heart Allocation policy, transplant recipients between 2018 and 2022 faced an approximately 20% increase in relative risk of dying or experiencing graft failure within three years compared with the pre-policy period. This is despite the ...
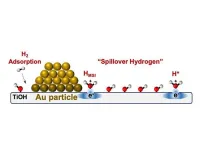
Striking gold with molecular mystery solution for potential clean energy
2023-09-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Hydrogen spillover is exactly what it sounds like. Small metal nanoparticles anchored on a thermally stable oxide, like silica, comprise a major class of catalysts, which are substances used to accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. The catalytic reaction usually occurs on the reactive — and expensive — metal, but on some catalysts, hydrogen atom-like equivalents literally spill from the metal to the oxide. These hydrogen-on-oxide species are called "hydrogen ...
Blood biomarker shows “great promise” predicting progression to Alzheimer’s disease in at-risk population
2023-09-01
DETROIT – Neuroscience researchers at Wayne State University published a review article that confirms the usefulness of neurofilament light (NfL) blood levels to predict the likelihood and rate of progression of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Blood-based NfL is a minimally invasive and easily accessible biomarker, making it a useful clinical biomarker. Youjin Jung and Jessica Damoiseaux, Ph.D., analyzed existing literature to examine the association between serum or plasma NfL and ...
Redo transcatheter aortic valve replacement proven effective, safe
2023-09-01
Cedars-Sinai investigators are leaders in the innovation and use of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) with balloon-expandable valves. They now show that redo TAVR procedures are both safe and effective when compared with situations in which patients with similar risk profiles undergo the same procedure for the first time.
The novel findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal The Lancet, are significant because recent randomized clinical trials have shown that TAVR is a meaningful treatment option for both younger and lower-risk surgical ...
Inflammation may influence weight loss surgery outcomes, new study reveals
2023-09-01
Research funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) has shown that higher levels of inflammation in the blood of patients with obesity undergoing bariatric surgery predicts poorer weight loss six months after the procedure.
Published in Psychological Medicine and led by researchers from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN), King’s College London, this is the first study to investigate the links between depression and inflammation in patients with obesity before and after bariatric surgery. The analysis showed a strong relationship ...
Study shows that low-dose aspirin associated with a 15% lower risk of developing diabetes in people aged over 65 years
2023-09-01
*Note- this is an early release from the Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) meeting in Hamburg, October 2-6. Please credit the meeting if you use this story*
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Hamburg, Germany (2-6 October) shows that use of low dose (100mg daily) aspirin among older adults aged 65 years and older is associated with a 15% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The authors, led by Professor Sophia Zoungas, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] COVID-19: Lessons from the PandemicWhy Sweden got it right, but most countries did not