A new NIR-PIT biomarker paves the way for targeted cancer treatments
2023-10-27
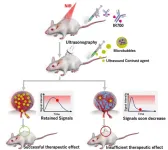
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan and their collaborators have used a biomarker based on microbubbles to evaluate the success of near-infrared photoimmunotherapy (NIR-PIT) treatment. Using ultrasound to track the microbubbles, they were able to identify areas where cancer therapy had not been fully applied. Their findings suggest ways to improve NIR-PIT and make it a viable alternative treatment for various types of cancer.
NIR-PIT is an innovative cancer treatment that combines the use of antibodies and near-infrared light to ...
Number of dementia cases could be 42% higher than previously estimated by 2040
2023-10-27
Up to 1.7 million people could be living with dementia in England and Wales by 2040 – over 40% more than previously forecast – finds a new UCL-led study.
Previous studies, based on data up to 2010, showed that dementia incidence had declined in high-income countries. However, the new research, published in The Lancet Public Health, indicates that dementia incidence started to increase in England and Wales after 2008.
Based on this estimated upward incidence trend, researchers project that the number of people with dementia in England and Wales may be significantly higher than expected in the future.
According to previous research* in England ...
Youngest children in class with ADHD as likely to keep diagnosis in adulthood as older pupils, find scientists
2023-10-27
Lancet Psychiatry study shows for first time that younger children are no more likely to lose ADHD diagnosis over time than older classmates
Experts in charge of study examined data from more than 6,500 patients with ADHD
360 million people worldwide have been diagnosed with the condition according to WHO – with around a third under the age of 18
Children who are the youngest in their class to be identified with ADHD are just as likely to keep the diagnosis as older pupils in their year group, scientists have found.
Experts from the University of Southampton ...
Effective treatment for rare sight-threatening infection
2023-10-27
A drug candidate, based on pioneering UCL and Moorfields Eye Hospital research and currently under development by SIFI S.p.A., has been found to be highly effective in treating a rare sight-threatening eye infection in a new international clinical trial.
The findings, published in Ophthalmology, describe the efficacy and safety of the first drug candidate for the treatment of Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK), applying a novel and evidence-based treatment protocol.
AK is one type of microbial keratitis (corneal infection) – a condition ...
Controlling waves in magnets with superconductors for the first time
2023-10-27
Quantum physicists at Delft University of Technology have shown that it’s possible to control and manipulate spin waves on a chip using superconductors for the first time. These tiny waves in magnets may offer an alternative to electronics in the future, interesting for energy-efficient information technology or connecting pieces in a quantum computer, for example. The breakthrough, published in Science, primarily gives physicists new insight into the interaction between magnets and superconductors.
Energy-efficient substitute
"Spin waves are waves in a magnetic material that we can use to transmit information," explains ...
$1.5 million DOD grant will create virtual reality test to assess TBI in the field
2023-10-27
One of the most common injuries sustained by military personnel in recent conflicts has been traumatic brain injury, or TBI. In response to this, and the fact that military operations are increasingly being conducted by small teams in far-flung areas, researchers in the University of Arizona College of Medicine – Tucson’s Department of Psychiatry are working on a portable virtual reality system to assess TBI in the field.
Psychiatry professor William “Scott” Killgore, PhD, and his team in the Social, ...
Antibody-drug conjugate helps patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer live longer, delaying disease progression
2023-10-27
Treatment with datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd), a novel Trop-2 directed antibody-drug conjugate, was found to significantly improve progression-free survival in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, an improvement that was primarily driven by patients with non-squamous tumors.
These results from the TROPION-Lung01 Phase III trial, which compared the standard of care in second-line docetaxel, a type of chemotherapy, with Dato-DXd, an antibody drug conjugate, in patients with pretreated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, were presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology 2023 Congress by Dr. Aaron ...
UTHSC cancer researcher part of $3 million collaborative project studying obesity-related cancer
2023-10-27
A University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC) researcher is a member of a prestigious team that has just received a highly competitive Endeavor Award totaling $3 million from The Mark Foundation for Cancer Research.
Liza Makowski, PhD professor in Hematology and Oncology at the UTHSC Center for Cancer Research, is a co-principal investigator on the award, which funds collaborative projects tackling complex challenges in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. Entitled “Inflammatory Drivers of The Obesity-Cancer Connection”, the project is led by principal ...
Common chemotherapy drugs don't work like doctors thought, with big implications for drug discovery
2023-10-27
A new study from the University of Wisconsin–Madison suggests that chemotherapy may not be reaching its full potential, in part because researchers and doctors have long misunderstood how some of the most common cancer drugs actually ward off tumors.
For decades, researchers have believed that a class of drugs called microtubule poisons treat cancerous tumors by halting mitosis, or the division of cells. Now, a team of UW–Madison scientists has found that in patients, microtubule poisons don't actually stop cancer cells from dividing. Instead, these drugs alter ...
SynGAP Research Fund awards $100,000 for investigating the impact of SYNGAP1 missense variants using structural bioinformatics
2023-10-26
TURKU, Finland – October 27, 2023 – The SynGAP Research Fund 501(c)(3) announced a $100,000 grant to researchers Pekka Postila and Olli Pentikäinen from the Institute of Biomedicine and InFLAMES Flagship at the University of Turku. Prof. Pentikäinen’s research focuses on molecular modeling and computer-aided drug discovery. Assoc. Prof. Postila is an expert on advanced molecular dynamics simulations of complex biomolecular systems. The dual research team was formed to study the structural effects of missense variants on the SynGAP protein, whose normal functioning ...
Something to chew on: Researchers look for connections in how animals eat and digest food
2023-10-26
Oct. 26, 2023
Media contacts:
Emily Gowdey-Backus, director of media relations, Emily_GowdeyBackus@uml.edu
Nancy Cicco, assistant director of media relations, Nancy_Cicco@uml.edu
UMass Lowell’s Nicolai Konow wants to bridge the gap between research on food processing and nutrient absorption.
“There is a divide between biomechanists, who study chewing and food transport, and physiologists, who examine what actually happens to food in the gastrointestinal tract,” said the assistant professor ...
Viral reprogramming of cells increases risk of cancers in HIV patients
2023-10-26
Viral infections are known to be a central cause of more than 10% of cancers worldwide. University of California researchers may have uncovered one of the key reasons why. Their findings were published today in PLOS Pathogens, a journal that reports groundbreaking work to advance understanding of how pathogens impact diseases such as cancer.
UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center researcher Yoshihiro Izumiya teamed up with Michiko Shimoda, who previously worked in the Izumiya Lab at UC Davis. Currently, she is a member of the Core Immunology Lab at UC San Francisco. Together, they led UC Davis researchers in the study of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). The ...
Robot stand-in mimics movements in VR
2023-10-26
Media Note: Pictures of VRoxy can be viewed and downloaded here: https://cornell.box.com/v/VRoxyrobotproxy
ITHACA, N.Y. – Researchers from Cornell and Brown University have developed a souped-up telepresence robot that responds automatically and in real-time to a remote user’s movements and gestures made in virtual reality.
The robotic system, called VRoxy, allows a remote user in a small space, like an office, to collaborate via VR with teammates in a much larger space. VRoxy represents the latest in remote, robotic embodiment.
Donning a VR headset, a user has access to two view modes: Live mode shows an immersive image of the ...
Major milestone achieved in new quantum computing architecture
2023-10-26
Coherence stands as a pillar of effective communication, whether it is in writing, speaking or information processing. This principle extends to quantum bits, or qubits, the building blocks of quantum computing. A quantum computer could one day tackle previously insurmountable challenges in climate prediction, material design, drug discovery and more.
A team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has achieved a major milestone toward future quantum computing. They have extended the coherence time for their novel type of qubit to an impressive 0.1 milliseconds — nearly a thousand times better than the previous record.
“Rather ...
"Recognition of human right to the environment can galvanize action and collaboration towards realization of sustainable development goals," eminent environmental lawyer says
2023-10-26
Amsterdam, October 26, 2023 – "The Human Right to the Environment affirms the right to life itself. When humans protect nature, they are also securing human health and wellbeing." An article by eminent environmental lawyer Prof. Nicholas A. Robinson sees the recognition of the Human Right to the Environment (HRE) as a first step in a long process of restoring a healthy environment for people and the planet.
Professor Robinson’s article is published in a special issue of the Journal of Environmental Policy and Law on The Human Right to Sustainable Environment. In the preface Editor-in-Chief Bharat H. Desai, PhD, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Centre ...
New tool measures food security duration, severity
2023-10-26
ITHACA, N.Y. – Researchers from the Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management have developed a new method for measuring food insecurity, which for millions of people in the U.S. is more than just an abstract concept.
The group’s probability of food security (PFS) measures the likelihood that a household’s food expenditures equal or exceed the minimum cost of a healthful diet. The researchers then put the PFS to the test, analyzing food security dynamics over a recent 17-year period, and found that a third of U.S. households experienced at least temporary food insecurity.
Seungmin Lee, a doctoral student in the field of applied economics and management, ...
Excess fluoride linked to cognitive impairment in children
2023-10-26
Long-term consumption of water with fluoride levels far above established drinking water standards may be linked to cognitive impairments in children, according to a new pilot study from Tulane University.
The study, published in the journal Neurotoxicology and Teratology, was conducted in rural Ethiopia where farming communities use wells with varying levels of naturally occurring fluoride ranging from 0.4 to 15.5 mg/L. The World Health Organization recommends fluoride levels below 1.5 mg/L.
Researchers ...
Scientists find two ways that hurricanes rapidly intensify
2023-10-26
Contacts:
David Hosansky, UCAR/NCAR Manager of Media Relations
hosansky@ucar.edu
720-470-2073
Audrey Merket, UCAR/NCAR Science Writer and Public Information Officer
amerket@ucar.edu
303-497-8293
Hurricanes that rapidly intensify for mysterious reasons pose a particularly frightening threat to those in harm’s way. Forecasters have struggled for many years to understand why a seemingly commonplace tropical depression or tropical storm sometimes blows up into a major hurricane, packing catastrophic winds and driving a potentially deadly surge of water ...
Is red meat intake linked to inflammation?
2023-10-26
Inflammation is a risk factor for many chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease (CVD), and the impact of diet on inflammation is an area of growing scientific interest. In particular, recommendations to limit red meat consumption are often based, in part, on old studies suggesting that red meat negatively affects inflammation – yet more recent studies have not supported this.
“The role of diet, including red meat, on inflammation and disease risk has not been adequately studied, which can lead to public health recommendations that are not based on strong evidence,” said Dr. Alexis Wood, associate professor of pediatrics – ...
RIT’s Campanelli receives award for work in gravitational wave science
2023-10-26
Rochester Institute of Technology distinguished professor and founding director of the Center for Computational Relativity and Gravitation Manuela Campanelli has been honored with the American Physical Society’s (APS) 2024 Richard A. Isaacson Award in Gravitational-Wave Science for her extraordinary contributions to and leadership in the understanding and simulation of merging binaries of compact objects in strong-field gravity.
The annual honor is granted to esteemed scientists for their remarkable achievements in the fields of gravitational-wave physics, gravitational wave astrophysics, and associated ...
Fruit, nectar, bugs and blood: How bat teeth and jaws evolved for a diverse dinnertime
2023-10-26
Link to full release with images:
https://www.washington.edu/news/2023/10/26/bat-teeth/
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
They don’t know it, but Darwin’s finches changed the world. These closely related species — native to the Galapagos Islands — each sport a uniquely shaped beak that matches their preferred diet. Studying these birds helped Charles Darwin develop the theory of evolution by natural selection.
A group of bats has a similar — ...
Mobile stroke units increase odds of averting stroke
2023-10-26
Receiving a clot-busting drug in an ambulance-based mobile stroke unit (MSU) increases the likelihood of averting strokes and complete recovery compared with standard hospital emergency care, according to researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine, NewYork-Presbyterian, UTHealth Houston, Memorial Hermann-Texas Medical Center and five other medical centers across the United States.
The study, published online in the Annals of Neurology on Oct. 6, determined that MSU care was associated with both increased odds of averting stroke compared with hospital emergency medical service (EMS) – ...
Why are so many migrant families still separated? Chaos in the data
2023-10-26
U.S. government reached a settlement with thousands of families separated under the zero-tolerance policy
Experts highlight ‘mountain of a challenge’ that U.S. Family Reunification Task Force has had in accounting for separations
Task force reuniting families is working within a limited scope of separated families
‘If using DNA data to reunite families could help even one child, it’s worth giving it a shot,’ says researcher
CHICAGO --- Five years since the retraction of the Trump-era zero-tolerance policy on illegal border crossings, which resulted in the separation ...
Mammalian cells may consume bacteria-killing viruses to promote cellular health
2023-10-26
Bacteriophages, also called phages, are viruses that infect and kill bacteria, their natural hosts. But from a macromolecular viewpoint, phages can be viewed as nutritionally enriched packets of nucleotides wrapped in an amino acid shell. A study published October 26th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Jeremy J. Barr at Monash University, Victoria, Australia, and colleagues suggests that mammalian cells internalize phages as a resource to promote cellular growth and survival.
Phage interactions with bacteria are well known, and interactions between bacteria and their mammalian host can lead ...
New research finds stress and strain changes metal electronic structure
2023-10-26
New research from the University of Birmingham shows that the electronic structure of metals can strongly affect their mechanical properties.
The research, published today (26th October) in the journal Science, demonstrates experimentally, for the first time, that the electronic and mechanical properties of a metal are connected. It was previously understood theoretically that there would be a connection, but it was thought that it would be too small to detect in an experiment.
Dr Clifford Hicks, Reader in Condensed Matter Physics, who worked on the study said: “Mechanical properties are typically described ...
[1] ... [1596]
[1597]
[1598]
[1599]
[1600]
[1601]
[1602]
[1603]
1604
[1605]
[1606]
[1607]
[1608]
[1609]
[1610]
[1611]
[1612]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.