How long should kids isolate after they’ve contracted COVID-19?
2023-10-23
School policies that require students with COVID-19 to stay out of the classroom for five days are more than sufficient. That’s because children infected with the Omicron variant remained infectious for a median time of three days after testing positive for the virus, according to a study by the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics and Stanford University.
“We're basically saying five days is more than sufficient; public-health and education leaders may consider shorter durations,” said co-author Neeraj ...
Homeless people are 16 times more likely to die suddenly
2023-10-23
A study led by UC San Francisco has found that people who are experiencing homelessness have a 16-fold higher rate of sudden death from heart attacks, as well as other causes.
The study focused on San Francisco County, which has one of the nation’s highest concentrations of homeless people. It found that the rate of sudden cardiac death was 7 times higher than the general population.
Some of these deaths may have been prevented with defibrillators and other public policy measures to improve health in this vulnerable population, according to the authors.
The paper published ...
New study shows surprising effects of fire in North America’s boreal forests
2023-10-23
A new study, using a first-of-its-kind approach to analyze satellite imagery from boreal forests over the last three decades, found that fire may be changing the face of the region in a way researchers did not previously anticipate.
Historically, fires in North American boreal forests have led to coniferous trees being supplanted by deciduous trees, which are faster growing, take up more carbon and reflect more light, leading to cooling of the climate and decreased likelihood of fire.
The study, led by Northern Arizona University and published today in Nature Climate Change, found that, surprisingly, while forests do become more deciduous, ...
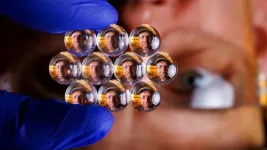
Chemists, engineers craft adjustable arrays of microscopic lenses
2023-10-23
They number in the thousands, light striking the phalanx of lenses arrayed on a face in geometric pattern, the beams refracting through transparent mounds no wider than a hair.
A fly’s eye boasts roughly 4,000 microscopic lenses, a honeybee’s up to twice that many. These lenses, though, belong not to a compound eye but to polydimethylsiloxane — a flexible polymer long ranking as a favored playground of Nebraska’s Stephen Morin and his band of fellow chemists.
With the aid of engineers Ruiguo Yang and Grayson Minnick, Morin’s team can now arrange and ...
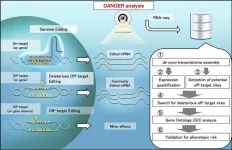
Researchers develop DANGER analysis tool for the safer design of gene editing
2023-10-23
A team of researchers has developed a software tool called DANGER (Deleterious and ANticipatable Guides Evaluated by RNA-sequencing) analysis that provides a way for the safer design of genome editing in all organisms with a transcriptome. For about a decade, researchers have used the CRISPR technology for genome editing. However, there are some challenges in the use of CRISPR. The DANGER analysis overcomes these challenges and allows researchers to perform safer on- and off-target assessments without a reference genome. It holds the potential for applications in medicine, agriculture, and biological research.
Their ...
Lung cancer outcomes significantly improved with immunotherapy-based treatment given before and after surgery
2023-10-23
HOUSTON ― A regimen of pre-surgical immunotherapy and chemotherapy followed by post-surgical immunotherapy significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) and pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared to chemotherapy alone for patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to results of a Phase III trial reported by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, were first presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
The AEGEAN trial evaluated durvalumab given perioperatively, meaning therapy ...
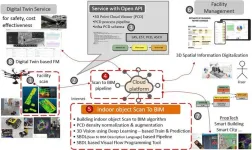
KICT develops scan to BIM for reverse engineering from 3D vision data
2023-10-23
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk) has developed building scan to BIM (Building Information Modeling)-based reverse engineering technology required for 3D geospatial information modeling domains such as digital twin information modeling.
Scan to BIM-based reverse engineering technology was studied to prevent errors and rework caused by manual work when modeling shapes or BIM from 3D scan data. Existing reverse engineering work is either done based on a lot of manual work or semi-automatically using expensive overseas software.
KICT Research Fellow Dr. Kang Tae-wook ...
Crystals brought back by astronauts show that the Moon is 40 million years older than scientists thought
2023-10-23
More than 4 billion years ago, when the Solar System was still young and the Earth was still growing, a giant object the size of Mars crashed into the Earth. The biggest piece that broke off of the early Earth formed our Moon. But precisely when this happened has remained a mystery. In a new study in the journal Geochemical Perspectives Letters, researchers used crystals brought back from the Moon by Apollo astronauts in 1972 to help pinpoint the time of the Moon’s formation. Their discovery pushes back the age of the Moon by 40 million years, to at least 4.46 billion years old.
“These ...
Probiotics delivered in biofilm state protect the intestines and brain in NEC model
2023-10-23
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a debilitating and deadly condition that affects infants who were born preterm. In NEC cases, intestinal tissues become inflamed, and in severe cases there is ischemia and death of the involved intestines. Treatment for NEC often involves surgery to remove the dying tissue.
“Even after decades of research, little has changed in terms of prognosis for infants who develop NEC,” says Gail Besner, MD, pediatric surgeon and principal investigator in the Center for Perinatal Research at Nationwide Children’s. ...
Heated yoga may reduce depression symptoms, according to recent clinical trial
2023-10-23
BOSTON – In a randomized controlled clinical trial of adults with moderate-to-severe depression, those who participated in heated yoga sessions experienced significantly greater reductions in depressive symptoms compared with a control group.
The results of the trial, which was led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), and was published in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, indicate that heated yoga could be a viable treatment option for patients with depression.
In the eight-week trial, 80 participants ...
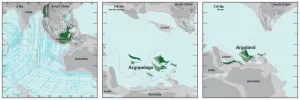
Finding Argoland: how a lost continent resurfaced
2023-10-23
Geologists have long known that around 155 million years ago, a 5000 km long piece of continent broke off western Australia and drifted away. They can see that by the ‘void’ it left behind: a basin hidden deep below the ocean known as the Argo Abyssal Plain. The underwater feature also lends its name to the newly formed continent: Argoland. The structure of the seafloor shows that this continent must have drifted off to the northwest, and must have ended up where the islands of Southeast Asia are located today. ...
Does diabetes affect the survival of individuals with colorectal cancer?
2023-10-23
Complications of diabetes can have numerous negative health effects, from impaired vision and nerve damage to kidney dysfunction and heart disease. In an analysis of information on adults with colorectal cancer, patients who also had diabetes—particularly those with diabetic complications—faced a higher risk of dying early. The results are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, Kuo‐Liong Chien, MD, PhD, of National Taiwan University, and his colleagues ...
Better regulation of mental health ‘therapies’ urgently needed to protect the vulnerable
2023-10-23
A rise in psychological pseudoscience is putting people at risk, psychologists have warned, with social media and celebrity endorsements partly to blame.
Mental health apps, mood-boosting supplements and energy therapies are among the therapies that could do ‘more harm than good’ according to psychologists Jonathan Stea and Stephen Hupp in their new book Investigating Clinical Psychology.
“As discourse around wellness, mental health, therapy, and access to these resources increasingly enter the public domain, the potential of coming across persuasive pseudoscience has also increased,” Stea explains.
“This is the age of health misinformation. It is everywhere. ...
Do people everywhere care less about their cats than their dogs?
2023-10-23
Do canines get more care? Some studies have suggested pet owners are less emotionally attached to and less willing to finance care for cats than dogs, possibly because of cats’ behavior: cats may be perceived as caring less about humans and needing less care in return. But these studies are often conducted on non-representative samples and don’t consider possible cultural differences in attitudes to pets. A team of scientists led by Dr Peter Sandøe of the University of Copenhagen decided to investigate further.
“We and others have found that people are willing to spend much less on their cats than ...
Association for Molecular Pathology appoints Lauren S. Menser as Chief Executive Officer
2023-10-23
ROCKVILLE, Md. – Oct. 23, 2023 – The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), the premier global molecular diagnostic professional society, today announced the appointment of Lauren S. Menser, CAE, as its Chief Executive Officer, effective January 3, 2024. Menser will succeed Mary Steele Williams, MNA, MT(ASCP)SM, CAE, after her retirement. AMP’s national search for a new executive leader was administered by an outside consulting firm and overseen by a diverse group of member volunteers.
Menser has served AMP in various capacities for more than 17 years. Since 2016, she has served as Director of Strategic Development, ...
Predictors of opioid overdose after prescription for chronic pain
2023-10-23
A large study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230459 identified 10 predictors of opioid overdose after prescription for chronic pain, which can help clinicians engage in shared decision-making with patients around opioid prescribing.
“The opioid crisis has generated interest in identifying patients at higher risk of addiction or overdose and has led to the development of several screening tools; however, these instruments have either not been validated or shown poor psychometric properties,” writes Dr. Li Wang, a researcher and methodologist at the ...
Plant-based isn't just about burgers anymore
2023-10-23
A team of University of Waterloo researchers has created smart, advanced materials that will be the building blocks for a future generation of soft medical microrobots.
These tiny robots have the potential to conduct medical procedures, such as biopsy, and cell and tissue transport, in a minimally invasive fashion. They can move through confined and flooded environments, like the human body, and deliver delicate and light cargo, such as cells or tissues, to a target position.
The tiny soft robots are a maximum of one centimetre long and are bio-compatible and non-toxic. The robots are made of advanced hydrogel ...
Better use of existing drugs increases cervical cancer survival and reduces recurrence
2023-10-22
The INTERLACE phase III trial, funded by Cancer Research UK and UCL Cancer Trials Centre, assessed whether a short course of induction chemotherapy (IC) prior to chemoradiation (CRT) could reduce the rate of relapse and death among patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. As part of an analysis of clinical data, the preliminary results will be presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) congress on Sunday 22 October 2023.
The peak incidence of cervical cancer is in women in their early thirties, with around 3,200 new cases each year in the UK. CRT has been the standard treatment for cervical cancer since 1999, but despite improvements ...
Adding immunotherapy to chemotherapy regimen improves survival in metastatic bladder cancer patients
2023-10-22
New York, NY (October 22, 2023) — A clinical trial co-led by Mount Sinai researchers is the first to show that using chemotherapy with immunotherapy resulted in improved survival in patients with an advanced type of bladder cancer. The results were simultaneously reported in The New England Journal of Medicine and at the annual meeting of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
The randomized phase 3 trial, named ”CheckMate 901,” showed significantly improved outcomes in patients who received the immunotherapy nivolumab with a combination of the chemotherapies gemcitabine and cisplatin, ...
Dual-action drug produces positive results in patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors, trial finds
2023-10-22
Cabozantinib, which targets tumor cell growth and tumor blood vessel growth, sharply improved progression-free survival over placebo in patients with extra-pancreatic and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Boston - A drug that simultaneously strikes cancer cells' growth circuits and pipeline to the bloodstream produced encouraging results in a clinical trial involving patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors, according to a study led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investigators.
Jennifer Chan, MD, MPH, director of the Program ...
Alliance presents detailed results from phase III CABINET pivotal Trial evaluating cabozantinib in advanced neuroendocrine tumors at ESMO 2023
2023-10-22
The Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology today announced detailed results will be presented at ESMO 2023 from CABINET (A021602), a phase III pivotal trial evaluating cabozantinib compared with placebo in two cohorts of patients with previously treated neuroendocrine tumors: one cohort of patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) and a second cohort of patients with advanced extra-pancreatic NET (epNET). The study met the primary objective for each cohort, demonstrating that cabozantinib provided dramatic improvements in median progression-free survival (PFS) for the patients in the pNET and epNET cohorts. ...
ESMO: Pre- and post-surgical immunotherapy improves outcomes for patients with operable lung cancer
2023-10-21
MADRID ― Compared with pre-surgical (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy alone, adding perioperative immunotherapy – given before and after surgery – significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) in patients with resectable early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Results from the Phase III CheckMate 77T study were presented today at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
At a median follow-up of 25.4 months, the median EFS with chemotherapy alone was 18.4 months, while the median had not yet been reached for patients receiving perioperative nivolumab, meaning EFS was prolonged ...
Kidney cancer study shows improved outcomes for patients with advanced disease when treated with belzutifan over everolimus
2023-10-21
Boston – Belzutifan significantly reduced the risk of progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), the most common type of kidney cancer, in patients previously treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-angiogenic therapies compared with everolimus in a phase 3 clinical trial. The trial, led by Toni K. Choueiri, MD, Director of the Lank Center for Genitourinary Cancer at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, showed the risk of progression was reduced by 25-26%.
The results were presented at the annual European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress on October ...
THE LANCET JOURNALS: Papers publishing during the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress 2023 (#ESMO 2023), 20th – 24th October 2023
2023-10-21
The following Lancet papers will be presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress 2023 (#ESMO 2023). The conference will take place between Friday 20th – Tuesday 24th October 2023.
Contact details for corresponding authors are provided should you wish to arrange an interview with the authors. Funding information is listed on the first page of each Article.
**Embargo: 13.00 [BST] / 14.00 [CEST] Friday 20th October 2023**
The Lancet: Pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: interim analyses from the phase ...
Highest risk patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma benefit from adjuvant everolimus
2023-10-21
A secondary analysis from the SWOG S0931 EVEREST trial has found that in the subgroup of patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) who were at very-high risk of recurrence, those who were treated with everolimus after surgery had a statistically significant improvement in recurrence-free survival compared to patients getting placebo after surgery.
The results will be presented at the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress 2023 in Madrid, Spain, on Oct. 23, 2023 (poster 1887P) by Primo N. Lara, Jr., MD, lead author on the abstract. ...
[1] ... [1595]
[1596]
[1597]
[1598]
[1599]
[1600]
[1601]
[1602]
1603
[1604]
[1605]
[1606]
[1607]
[1608]
[1609]
[1610]
[1611]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.