JMIR Infodemiology call for papers theme issue on misinformation and generative AI
2023-10-25
JMIR Infodemiology Editor-in-Chief: Tim Ken Mackey, MAS, PhD welcomes submissions to a special theme issue “Exploring the Intersection Between Health Information, Disinformation, and Generative AI Technologies.”
JMIR Infodemiology, currently indexed in PubMed Central, PubMed, Scopus, DOAJ, and CABI, is a peer-reviewed premier journal in the field of infodemiology, health information, data science, and misinformation and is inviting submissions from different disciplines of health communication, public health, informatics, data science, social ...
Yale School of Nursing receives historic gift for scholarships
2023-10-25
Yale School of Nursing (YSN) has received a landmark gift — the largest single donation in the school’s history. The $11.1 million gift from a generous anonymous donor was announced on Sept. 21 by Azita Emami, dean of the Yale School of Nursing, at an event kicking off the school’s yearlong centennial celebration (September 2023–May 2024).
This endowed gift will support the YSN Community Scholars program, providing full-tuition scholarships to six students each year in the Master of Science in Nursing ...
Birmingham rare earth magnet recycling technology selected as a Minerals Security Partnership project
2023-10-25
A Principals’ meeting of the Minerals Security Partnership (MSP) has confirmed that HyProMag Ltd, which uses a technology developed by the University of Birmingham’s Magnetic Materials Group has been selected as one of the projects that will help to develop responsible critical mineral supply chains.
Formed in 2022 by 14 governments, the Mineral Security Partnership (MSP) aims to ensure adequate supplies of minerals such as rare earths to meet net zero-carbon goals. It aims to support public and private sector investments building diverse, secure, and responsible global critical minerals supply chains.
HyProMag was one ...
Novel small molecule 5D4 disrupts several molecular pathways, including MYC, that lead to cancer growth
2023-10-25
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have identified a small molecule named 5D4 that can suppress the growth of breast and ovarian cancers in animal models. 5D4 works by binding to TopBP1 protein in cancer cells, disrupting its interactions with several pathways that promote cancer growth. Combining 5D4 with another cancer inhibitor, talazoparib, enhances the effectiveness of the anti-cancer activity. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, strongly supports continuing the investigation toward further developing this strategy for clinical use.
“Cancer development involves many steps of genetic alterations and signaling ...
Unlocking pathways to break down problem proteins presents new treatment opportunities
2023-10-25
When targeting problem proteins involved in causing or spreading disease, a drug will often clog up a protein’s active site so it can’t function and wreak havoc. New strategies for dealing with these proteins can send these proteins to different types of cellular protein degradation machinery such as a cell’s lysosomes, which act like a protein wood chipper.
In a new study published in Science on Oct. 20, Stanford chemists have uncovered how one of the pathways leading to this protein “wood chipper” works. In doing so, they have opened the ...
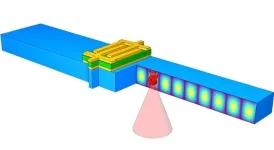
Using sound to test devices, control qubits
2023-10-25
Acoustic resonators are everywhere. In fact, there is a good chance you’re holding one in your hand right now. Most smart phones today use bulk acoustic resonators as radio frequency filters to filter out noise that could degrade a signal. These filters are also used in most Wi-Fi and GPS systems.
Acoustic resonators are more stable than their electrical counterparts, but they can degrade over time. There is currently no easy way to actively monitor and analyze the degradation of the material quality of these widely used devices.
Now, researchers at the Harvard John ...
Oregon State researchers uncover mechanism for treating dangerous liver condition
2023-10-25
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A study spearheaded by Oregon State University has shown why certain polyunsaturated fatty acids work to combat a dangerous liver condition, opening a new avenue of drug research for a disease that currently has no FDA-approved medications.
Scientists led by Oregon State’s Natalia Shulzhenko, Andrey Morgun and Donald Jump used a technique known as multi-omic network analysis to identify the mechanism through which dietary omega 3 supplements alleviated nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, usually abbreviated to NASH.
The mechanism involves ...
More than just carbs: starchy vegetables play an integral role in meeting nutrition needs
2023-10-25
A perspective recently published in Frontiers in Nutrition underscores the unique role starchy vegetables play as a vital vehicle for essential nutrients. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans currently recommend that most adults consume five to six cups (or cup equivalents) of starchy vegetables each week to help meet their total vegetable goals.1 Yet, as confusion around “good versus bad carbs” persists among consumers, there is a risk of starchy vegetable avoidance in favor of other carbohydrate foods perceived as ...
Study suggests that having common ancestors can jeopardize fertility for generations
2023-10-25
When it comes to the architecture of the human genome, it’s only a matter of time before harmful genes — genes that could compromise future generations — arise in a population. These mutations accumulate in the gene pool, primarily affected by a population’s size and practices like marrying within a small community, according to researchers.
But much of the information about the effects of a population’s mutation load is based on genetic theory, with limited direct evidence concerning the effects on evolutionary fitness, or fertility.
New research from University ...
Zooming in on our brains on Zoom
2023-10-25
New Haven, Conn. — When Yale neuroscientist Joy Hirsch used sophisticated imaging tools to track in real time the brain activity of two people engaged in conversation, she discovered an intricate choreography of neural activity in areas of the brain that govern social interactions. When she performed similar experiments with two people talking on Zoom, the ubiquitous video conferencing platform, she observed a much different neurological landscape.
Neural signaling during online exchanges was substantially suppressed compared to activity observed ...
Breaking down the bias: the portrayals of women in medicine in films
2023-10-25
In the 2009 film "Gifted Hands," based on a true story, the audience follows Black neurosurgeon Dr. Ben Carson as he successfully performs three risky surgeries, earning praise from the media and medical community. This movie was not only a hit with critics and audiences, but it also inspired Bismarck Christian Odei, MD, an assistant professor in radiation oncology at Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah, to follow his passion.
“Seeing a physician who looked like me, ...
Many in law enforcement own firearms. They are more likely to have suicidal thoughts
2023-10-25
Law enforcement officers in the United States own firearms at high rates and rarely engage in secure firearm storage, which could increase their risk for suicide, according to a Rutgers study.
The researchers, whose study appears in the journal Injury Prevention, examined data from 369 law enforcement officers in the U.S. Information about firearm ownership, storage, suicide risk and demographics were included in the present study.
Overall, 70.5 percent of law enforcement officers report owning a firearm. The most common type of firearms owned were handguns (79.7 percent) followed by shotguns (61.1 percent) and rifles (57.5 percent). A sharp majority, 78.9 percent, ...
Rider on the storm: Shearwater seabird catches an 11 hour ride over 1,000 miles in a typhoon
2023-10-25
New research from Japan published in the Ecological Society of America’s journal Ecology suggests that increasingly severe weather driven by climate change may push oceangoing seabirds to their limits.
In August 2019, Kozue Shiomi, a seabird biologist at Tohoku University, attached GPS bio-loggers to 14 adult streaked shearwaters (Calonectris leucomelas) from a nesting colony on Mikurajima, a small island near Tokyo, as part of a study on the species homing behavior.
In September of that same year, an exceptionally powerful storm, Typhoon Faxai, barreled into southeastern Japan, causing considerable physical damage to the mainland. But the typhoon, ...
Morris Animal Foundation-backed research illuminates path to sihek revival
2023-10-25
DENVER/Oct. 25, 2023 – A recently published paper in Animal Conservation provides crucial insights into the health of sihek, a species eradicated from its native habitat and that may now face threats in captivity. The latest data underscores a stark gender disparity, revealing that female sihek are at greater risk for death and disease than their male counterparts.
As part of an ongoing Morris Animal Foundation-funded study, researchers at The Zoological Society ...
Can insomnia treatment reduce cardiovascular disease risks? $3 million funds study to find out
2023-10-25
INDIANAPOLIS — It’s no secret that a good night’s rest can do wonders for one’s health, but those who struggle with insomnia have a nearly 50% increased risk of cardiovascular disease. One scientist in the School of Science at IUPUI will spend the next five years trying to figure out how those risks can be reduced.
Jesse Stewart, a professor of psychology at the school, has received a five-year, $3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute for a project named the Strengthening Hearts ...
Higher levels of triglycerides linked to lower risk of dementia
2023-10-25
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 25, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Older people who have higher levels of triglycerides, a type of fat, may have a lower risk of dementia and a slower cognitive decline over time compared to people who have lower levels, according to new research published in the October 25, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. While the study found a link, it does not prove that higher levels of triglycerides prevent dementia.
Triglycerides are fatty acids and are the most common type of fat in the blood. Triglycerides contribute ...
Childhood trauma linked to headaches in adulthood
2023-10-25
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 25, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have experienced traumatic events in childhood such as abuse, neglect or household dysfunction may be more likely to experience headache disorders as adults, according to a meta-analysis published in the October 25, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. This research does not prove that such experiences cause headaches; it only shows an association.
“Traumatic events in childhood can have ...
Brittle star fossils found in South Africa are over 410 million years old, the oldest known examples who lived at high latitude
2023-10-25
Brittle star fossils found in South Africa are over 410 million years old, the oldest known examples who lived at high latitude
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0292636
Article Title: Earliest known ophiuroids from high palaeolatitude, southern Gondwana, recovered from the Pragian to earliest Emsian Baviaanskloof Formation (Table Mountain Group, Cape Supergroup) South Africa
Author Countries: South Africa, Luxembourg
Funding: RWG: Millennium Trust, South Africa (no number). https://www.mtrust.co.za ...
New distractibility “d factor” may be linked with ADHD
2023-10-25
In a study of different types of distraction involving more than 1,000 participants, researchers statistically derived a novel measure—dubbed the “d factor”—that could represent a person’s general tendency towards distraction and may be linked with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Han Zhang of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 25, 2023.
Prior research has explored various types of distraction, such as external stimulations, repetitive ...
Deepfake videos during Russian invasion of Ukraine could undermine trust
2023-10-25
A new study explores themes in Twitter discussions of deepfake videos related to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, highlighting the potential for real videos to be mistaken for deepfakes and for deepfakes to fuel conspiracy theories. John Twomey of University College Cork, Ireland, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 25, 2023.
Created using artificial intelligence, deepfake videos typically feature a person saying and doing things they never actually did in real life. Deepfake technology has advanced considerably, sparking concerns about its potential harms. ...
In Prehispanic Cancun, immigrants were treated just like Maya locals
2023-10-25
Ancient people immigrated to Cancun Island and were treated just like locals, according to a study published October 25, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Andrea Cucina of the Autonomous University of Yucatan, Mexico and colleagues.
The Late Postclassic (AD 1200-1500) in the northern Maya lowlands was a period of major changes, including the development of many settlements along the east coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, influenced in part by expanded trade routes. Previous research has found that these settlements were home to many non-local individuals, but it remains unclear whether these people were treated as “foreigners” ...
Climate change likely impacted human populations in the Neolithic and Bronze Age
2023-10-25
Human populations in Neolithic Europe fluctuated with changing climates, according to a study published October 25, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ralph Großmann of Kiel University, Germany and colleagues.
The archaeological record is a valuable resource for exploring the relationship between humans and the environment, particularly how each is affected by the other. In this study, researchers examined Central European regions rich in archaeological remains and geologic sources of climate data, using these resources to identify correlations between human population trends and climate change.
The ...
First ever study of wartime deepfakes reveals their impact on news media
2023-10-25
A first ever study of wartime deepfake videos reveals their impact on news media and outlines implications for social media companies, media organisations and governments.
Deepfakes are artificially manipulated audio-visual material. Most deepfake videos involve the production of a fake ‘face’ constructed by Artificial Intelligence, that is merged with an authentic video, in order to create a video of an event that never really took place. Although fake, they can look convincing and are often produced to imitate or mimic an individual.
Researchers at University ...
Anti-anxiety drug may improve brain cancer survival chances
2023-10-25
A new research study shows that cerebrospinal fluid reduces current treatment efficacy in brain cancer and identifies new therapeutic opportunities.
Cerebrospinal fluid, the clear colourless liquid that protects the brain, also may be a factor that makes brain cancers resistant to treatment, Australian researchers led by Associate Professor Cedric Bardy at the South Austraila Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI) and Flinders University reveal in the journal Science Advances.
Reporting how this occurs, the study in high-profile journal Science Advances shows that a decades-old anti-anxiety drug can improve the effectiveness of chemo-radiotherapy ...
Something in the eyes: Java Sparrows in love show enhanced eye rings
2023-10-25
Pair-bonded Java sparrows show enlarged eye rings to signal breeding readiness.
Birds are known for their elaborate courtship rituals and romantic gestures that are replete with beautiful songs, complex dances, gift-giving practices, preening, and flamboyant plumage. While changes in colorful external attributes during this period has attracted much attention, the role of facial features remains an under-investigated aspect of this behavior.
Associate Professor Masayo Soma and her research group at the Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University, reported increased swelling in Java sparrows’ eye rings—an area of blushed bare skin around the eyes—upon ...
[1] ... [1600]
[1601]
[1602]
[1603]
[1604]
[1605]
[1606]
[1607]
1608
[1609]
[1610]
[1611]
[1612]
[1613]
[1614]
[1615]
[1616]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.