Scientists uncover new way viruses fight back against bacteria
2023-10-18
A microscopic discovery will not only enable scientists to understand the microbial world around us but could also provide a new way to control CRISPR-Cas biotechnologies.
An international team of researchers led by Professor Peter Fineran from the University of Otago and Dr Rafael Pinilla-Redondo from the University of Copenhagen has published a study in the prestigious journal Nature revealing new way viruses suppress the CRISPR-Cas immune systems of bacteria.
Co-first author Dr David Mayo-Muñoz, of the Phage-host interactions (Phi) laboratory in ...
Single vaccine protects against three deadly strains of coronavirus
2023-10-18
DURHAM, N.C. – A vaccine designed to protect against three different deadly coronaviruses shows success in mouse studies, demonstrating the viability of a pan-coronavirus vaccine developed by researchers at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute.
Publishing in the journal Cell Reports, the single nanoparticle vaccine included components of a previous vaccine that was shown to protect mice and primates against multiple variants of SARS-CoV-2, which is the virus that causes COVID-19. In this study, the vaccine protected mice from SARS-CoV-1, another form of SARS coronavirus that can infect humans, and a MERS coronavirus that has led to periodic, deadly outbreaks ...
Milestone: Miniature particle accelerator works
2023-10-18
Particle accelerators are crucial tools in a wide variety of areas in industry, research and the medical sector. The space these machines require ranges from a few square meters to large research centers. Using lasers to accelerate electrons within a photonic nanostructure constitutes a microscopic alternative with the potential of generating significantly lower costs and making devices considerably less bulky. Until now, no substantial energy gains were demonstrated. In other words, it has not been shown that electrons really have increased in speed significantly. A team of laser physicists at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg ...
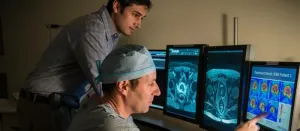
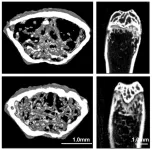
Simple MRI scan could predict radiation side effects for prostate cancer
2023-10-18
A new Corewell Health study suggests that men who have longer prostatic urethras, the part of the urethra that travels through the prostate, may be at a higher risk of experiencing moderate, often chronic urinary side effects after receiving radiation for prostate cancer.
To date, researchers have struggled to determine any risk factors that could shed light on who might experience these types of side effects ahead of time. But now, a simple MRI scan and a new metric to determine urethra length could change that.
Results, now published in the journal Academic Radiology, indicate that for every 1-centimeter increase in length of the prostatic ...
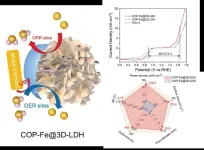
A newly hierarchically porous pyrolysis-free bifunctional catalyst to boost ultralong lifespan zinc-air batteries
2023-10-18
They published their work on Oct. 12 in Energy Material Advances.
"The development of cost-effective and high-performance zinc-air battery cathode catalyst is imperative," said paper author Zhonghua Xiang, professor with the Beijing University of Chemical Technology. "Currently, zinc-air batteries still not occupy the market, because they are limited in both stability and in their energy density."
Xiang explained that zinc-air batteries can only work for very limited time at high current density, because there are lots of problems of its cathode, anode and electrolyte.
"The air ...
Do adult periodical cicadas actually feed on anything?
2023-10-18
Annapolis, MD; October 18, 2023—Every so often, cicadas emerge above ground and blanket the earth with their exoskeletons while emitting a high-pitched chirp from sunrise to sunset. The periodical cicadas in the genus Magicicada come every 13 or 17 years, though other types of cicadas emerge much more frequently in our neighborhoods. A long-standing agricultural query related to the periodical cicadas was recently answered by an Agricultural Research Service (USDA-ARS) research team at West Virginia's Appalachian Fruit Research Station. Simply: Once periodical ...
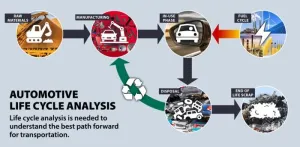
SwRI to host Life-Cycle Analysis for Transportation Symposium Nov. 16-17
2023-10-18
SAN ANTONIO — October 18, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute will host the Life-Cycle Analysis for Transportation Symposium on Nov. 16-17 in San Antonio. This year’s symposium will be in person for the first time.
The two-day event will highlight academic, industry and institutional research efforts to characterize the total greenhouse gas emissions produced during the entire life cycle of a vehicle, including its manufacture, service life and recycling or disposal.
“We often talk about getting to ‘zero-emissions,’ but this definition often ...
ASHG 2023 Annual Meeting to welcome thousands of researchers in Washington, DC to advance human genetics and genomics discoveries and applications
2023-10-18
Media Contact: Kara Flynn, 202.257.8424, press@ashg.org
For Immediate Release: Wednesday, October 18, 2023, 10:00am U.S. Eastern Time
ROCKVILLE, MD — More than ever before, human genetics and genomics is an essential part of making progress in research, biotechnology, and health. As a key leader supporting research innovation, the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) will convene more than 8,000 researchers and clinicians at the ASHG 2023 Annual Meeting in Washington DC, Nov. 1-5 to share emerging discoveries and celebrate the Society’s 75th anniversary.
“Human genetics is transforming science and health at a rapid ...
Map: Wildlife polluted by flame retardants on massive scale
2023-10-18
More than 150 species of wild animals across every continent are contaminated with flame retardant chemicals, according to a new map tracking peer-reviewed research worldwide. Polluted wildlife include killer whales, red pandas, chimpanzees and other endangered species. Added to furniture, electronics, vehicles, and other everyday products to meet flammability standards, the chemicals often do not work as intended. They also migrate out of products and into wildlife—and people.
“Flame retardants don’t actually make TV enclosures and car interiors more fire-safe, but they can harm people and animals,” ...
New insights into the genetics of the common octopus: genome at the chromosome level decoded
2023-10-18
Octopuses are fascinating animals – and serve as important model organisms in neuroscience, cognition research and developmental biology. To gain a deeper understanding of their biology and evolutionary history, validated data on the composition of their genome is needed, which has been lacking until now. Scientists from the University of Vienna together with an international research team have now been able to close this gap and, in a study, determined impressive figures: 2.8 billion base pairs - organized in ...
Researchers unveil fire-inhibiting nonflammable gel polymer electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries
2023-10-18
A collaborative research team, led by Professor Hyun-Kon Song in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, Dr. Seo-Hyun Jung from Research Center for Advanced Specialty Chemicals at Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT), and Dr. Tae-Hee Kim from the Ulsan Advanced Energy Technology R&D Center at Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER), has achieved a groundbreaking milestone in battery technology. Their remarkable achievement in developing a non-flammable gel polymer electrolyte (GPE) is set to revolutionize the safety of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) by ...
Test of police implicit bias training shows modest improvements
2023-10-18
SPOKANE, Wash. – A two-part training designed to help police officers recognize their implicit bias, revealed some behavior improvement and lowered citizen discrimination complaints in a controlled study. While a small study involving one police department, it is the first-known research to provide evidence that this type of training can produce positive behavioral effects.
Led by Washington State University researcher Lois James, the study found some improvement in the anti-bias trained officers’ behavior toward homeless people in particular, ...
Wearable device makes memories and powers up with the flex of a finger
2023-10-18
Researchers have invented an experimental wearable device that generates power from a user’s bending finger and can create and store memories, in a promising step towards health monitoring and other technologies.
The innovation features a single nanomaterial incorporated into a stretchable casing fitted to a person’s finger. The nanomaterial enabled the device to generate power with the user bending their finger.
The super-thin material also allows the device to perform memory tasks, as outlined below.
Multifunctional devices normally require several materials in layers, which involves the time-consuming challenge of stacking nanomaterials with high precision.
The team, led ...
AI and 10 seconds of voice can screen for diabetes, new study reveals
2023-10-18
Determining whether a person is diabetic could be as easy as having them speak a few sentences into their smartphone, according to a groundbreaking study from Klick Labs that combines voice technology with artificial intelligence in a major step forward in diabetes detection.
The new study, published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health, outlines how scientists used six to 10 seconds of people’s voice, along with basic health data, including age, sex, height, and weight, to create an AI model ...
AI identifies antimalarial drug as possible osteoporosis treatment
2023-10-18
Correction (Oct. 17, 2023): The paper’s title has been corrected to “Deep Learning-Predicted Dihydroartemisinin Rescues Osteoporosis by Maintaining Mesenchymal Stem Cell Stemness through Activating Histone 3 Lys 9 Acetylation
Artificial intelligence has exploded in popularity and is being harnessed by some scientists to predict which molecules could treat illnesses, or to quickly screen existing medicines for new applications. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have used one such deep learning algorithm, and found that dihydroartemisinin ...
Simplifying the generation of three-dimensional holographic displays
2023-10-18
Holograms that offer a three-dimensional (3D) view of objects provide a level of detail that is unattainable by regular two-dimensional (2D) images. Due to their ability to offer a realistic and immersive experience of 3D objects, holograms hold enormous potential for use in various fields, including medical imaging, manufacturing, and virtual reality. Holograms are traditionally constructed by recording the three-dimensional data of an object and the interactions of light with the object. However, this technique is computationally highly intensive as it requires ...
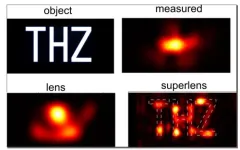
Superlensing without a super lens: physicists boost microscopes beyond limits
2023-10-18
Ever since Antonie van Leeuwenhoek discovered the world of bacteria through a microscope in the late seventeenth century, humans have tried to look deeper into the world of the infinitesimally small.
There are, however, physical limits to how closely we can examine an object using traditional optical methods. This is known as the ‘diffraction limit’ and is determined by the fact that light manifests as a wave. It means a focused image can never be smaller than half the wavelength of light used to observe an object.
Attempts to break this limit with “super lenses” have all hit the hurdle of extreme visual losses, making the lenses opaque. ...
Collaborative study focuses on using computer algorithms to find molecular adaptations to improve COVID-19 drugs
2023-10-18
As the COVID-19 pandemic scattered and isolated people, researchers across Virginia Tech connected for a data-driven collaboration seeking improved drugs to fight the disease and potentially many other illnesses.
A multidisciplinary collaboration spanning several colleges at Virginia Tech resulted in a newly published study, “Data Driven Computational Design and Experimental Validation of Drugs for Accelerated Mitigation of Pandemic-like Scenarios,” in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
The study focuses on using computer algorithms to generate adaptations to ...
Study predicts potential for 110% electricity increases in U.S. urban buildings
2023-10-18
A research study led by University of Oklahoma assistant professor Chenghao Wang and recently published in the journal Nature Communications tackled the critical issue of how city-scale building energy consumption in urban environments will evolve under the influence of climate change.
Fossil fuels account for approximately 40% of all building energy use in urban city centers in the United States, and the U.S. Energy Information Administration reports that residential and commercial buildings in U.S. cities are one of the major energy ...
Open access: Need to move away from transformative agreements
2023-10-18
Sweden is far ahead when it comes to promoting open access to scholarly publications. But there is risk of getting stuck in a permanent transformation that favours large commercial publishers. A new report from the Association of Swedish Higher Education Institutions develops a strategy on how to work in negotiations with the publishers.
In 2021, the Association of Swedish Higher Education Institutions (Sveriges universitets- och högskoleförbund, SUHF) convened a “Beyond transformative agreements” working group (the BTA group) to lay the foundation for further advancing the transition to open access. Now, the group ...
Graz University of Technology study on e-scooter accidents: more helmets and less speed reduce the injury risk
2023-10-18
The use of e-scooters has increased significantly in recent years, but so has the number of accidents involving this relatively new form of transport. At the same time, knowledge about injury mechanisms in this area was still very limited. In the project SURF, funded by Zukunftsfonds Steiermark, the Vehicle Safety Institute at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) investigated this topic using Human Body Models and derived recommendations to reduce the injury risk in e-scooter accidents.
Put on a helmet, decrease speed and get off the pavement
As ...
Reef-devouring predator survives coral bleaching and feasts on the survivors
2023-10-18
Research conducted by marine biologists from the University of Sydney has found juvenile crown-of-thorns starfish can withstand tremendous heatwaves well above levels that kill coral. These starfish then develop into carnivorous predators that devour reefs just as they begin to regrow.
Crown-of-thorns starfish are native to the Great Barrier Reef and found in the Indo-Pacific region, but they are classified as a species of concern because the damage large populations cause to coral is more significant than any other species. ...
Does SARS-CoV-2 infection have urological effects?
2023-10-18
Research published in the Journal of Internal Medicine indicates that SARS-CoV-2 infection may worsen lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men.
The study included 17,986 men receiving medication for LUTS within the public healthcare system of Hong Kong in 2021–2022, half of whom had SARS-CoV-2 infection. The group with SARS-CoV-2 had significantly higher rates of retention of urine (4.55% versus 0.86%); blood in the urine (1.36% versus 0.41%); clinical urinary tract infection (4.31% versus 1.49%); bacteria in the urine (9.02% versus 1.97%); and addition of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which are drugs prescribed for enlarged prostate. (0.50% versus 0.02%). These urological ...
How did the initial COVID-19 wave affect mental health in the UK?
2023-10-18
New research published in Economic Inquiry reports substantial increases in psychological distress in the UK during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mental health effects were more pronounced for females; younger individuals; Black, Asian, and minority ethnic communities; and migrants. Also, people who had financial worries, loneliness, or were living in overcrowded dwellings experienced significantly worse mental health deterioration during the first wave.
The study used data from the UKHLS, also known as Understanding Society, which is a household panel dataset that captures, among other things, information from adults about their economic and social circumstances, ...
Heat-tolerant predatory sea stars will likely be a threat to coral during climate change
2023-10-18
Population outbreaks of the crown-of-thorns sea star (COTS), a predator of coral, can cause widespread coral mortality. COTS are herbivorous as juveniles but then switch to coral consumption as they grow to adulthood. When researchers exposed juvenile COTS to heat stress scenarios at time and temperature durations designed to reflect conditions that cause coral bleaching and mortality, juveniles exhibited tolerance to heatwave conditions well above levels that kill coral.
The findings, which are published in Global Change Biology, indicate that juvenile COTS are likely to persist as major coral predators in reefs already vulnerable to the effects of climate change.
“This ...
[1] ... [1604]
[1605]
[1606]
[1607]
[1608]
[1609]
[1610]
[1611]
1612
[1613]
[1614]
[1615]
[1616]
[1617]
[1618]
[1619]
[1620]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.