GPM sees rainfall in Tropical Depression Kilo nearing Johnston Island
2015-08-24
(Press-News.org) The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM mission core satellite gathered rainfall data on Tropical Depression Kilo as it heads toward Johnston Island in the Central Pacific Ocean. On August 24, a Tropical Storm Warning was posted for Johnston Island
Kilo formed as depression and strengthened into a tropical storm to southeast of the Hawaiian Islands on August 20, 2015. By 5 a.m. EDT on Sunday, August 23, Kilo weakened to a tropical depression. Today, August 24, the tropical depression nearing Johnston Island.
The National Hurricane Center noted that Johnston Island will experience tropical storm conditions today and tomorrow, August 25. Large surf is expected especially along east and southeast facing reefs and shorelines through Wednesday, August 25, and Kilo is expected to drop between 4 to 8 inches of rainfall along and near its track.
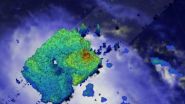
That rainfall was seen by the GPM core observatory satellite on August 23, 2015 at 0131 UTC (Aug. 22 at 11:31 p.m. EDT). GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) discovered that rain was falling at a rate of over 121 mm (4.8 inches) in powerful storms on the northern side of Kilo. Those same storms are shown in a 3-D simulated view reaching heights of over 16.6 km (10.3 miles). The GPM satellite is managed by NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
On August 24 at 1200 UTC (8 a.m. EDT), the center of Tropical Depression Kilo was located near latitude 14.8 north and longitude 166.7 west. That's about 160 miles (255 km) east of Johnston Island the Depression is moving toward the west-northwest near 7 mph (11 kph). The estimated minimum central pressure is 1006 millibars. Maximum sustained winds are near 35 mph (55 kph). For updated forecasts, visit NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center website: http://www.prh.noaa.gov/cphc.
Kilo is expected to strengthen to a tropical storm later today and into a hurricane by Tuesday, August 25 as it turns northeast toward the island of Nihoa.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-24
Washington D.C., August 24, 2015 - Children who have been abused typically experience more intense emotions than their peers who have not been abused. This is often considered a byproduct of living in volatile, dangerous environments. A recent study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP) set to find out what happens when these children are taught how to regulate their emotions. Could that better help them cope with difficult situations?
The team of researchers from the University of Washington studied what happens ...
2015-08-24
WASHINGTON, Aug. 24 2015 -- You're tired and you need an energy boost, but you don't want the jitters from caffeine. What to do? In this Reactions video, we give you some chemistry-backed tips -- one of which involves cats -- to boost your productivity and stay awake without refilling the coffee cup. Check it out here: https://youtu.be/SvEQBURrPow
INFORMATION:
Subscribe to our weekly series at http://bit.ly/ACSReactions and follow us on Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 158,000 ...
2015-08-24
We humans have been using self-medication to cure the illnesses since the dawn of our species. There is some evidence that also other animals can exhibit this type of behavior, but the evidence has been hard to come by.
Scientists from the University of Helsinki, Finland, have now shown that black ant Formica fusca can change their taste for food once exposed to the fungal pathogens. In the compound of interest was hydrogen peroxide, which can be found in the damaged plants, other insects and cadavers.
"When ants are feeding on the diet containing extra free radicals ...
2015-08-24
People are motivated to participate in the sharing economy because of its ecological sustainability, the enjoyment derived from the activity, the sense of community, and saving money and time. Ecological sustainability is one of the basic principles of the sharing economy - not to purchase everything individually but rather consumer collaboratively by sharing goods and services. Another canonical principle of the sharing economy is 'paying it forward'. However, collaborative consumption may involve the same hurdles as any other type of green consumption, researcher from ...
2015-08-24
The report, published on F1000Research and titled Neuropathic pain in a patient with congenital insensitivity to pain has just passed peer review. It concerns a unique case of a woman with Channelopathy-associated Insensitivity to Pain (CIP) Syndrome, who developed features of neuropathic pain after sustaining pelvic fractures and an epidural hematoma that impinged on the right fifth lumbar (L5) nerve root. These injuries were sustained during a painless labour, which culminated in a Caesarean section.
The patient had been diagnosed with CIP as child. This was later ...
2015-08-24
CINCINNATI - A study published online Aug. 24 by the journal Pediatrics finds a significant decrease in the use of computed tomography (CT) scans at children's hospitals for 10 common childhood diagnoses including seizure, concussion, appendectomy and upper respiratory tract infection.
Alternate types of imaging such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are being used more frequently for eight of the 10 diagnoses. Study authors hypothesize the decline in CT usage may be attributable to a growing body of evidence linking ionizing radiation from CT scans to ...
2015-08-24
Yes, a good cry indeed might go a long way to make you feel better, says Asmir Gračanin of the University of Tilburg in the Netherlands, lead author of a study in Springer's journal Motivation and Emotion. These findings were established after a research team videotaped a group of participants while watching the emotionally charged films La vita è bella and Hachi: A Dog's Tale. Afterwards, the participants were asked a few times to reflect on how they felt.
Although humans are the only species able to shed emotional tears, little is known about the function ...
2015-08-24
21.08.2015: In mountainous regions earthquakes often cause strong landslides, which can be exacerbated by heavy rain. However, after an initial increase, the frequency of these mass wasting events, often enormous and dangerous, declines, in fact independently of meteorological events and aftershocks. These new findings are presented by a German-Franco-Japanese team of geoscientists in the current issue of the journal Geology, under the lead of the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences. Even after strong earthquake the activity of landslides returns back over the course ...
2015-08-24
By minimizing the acceleration of industrial robots, energy consumption can be reduced by up to 40 percent - while retaining the given production time. This is the result of a new optimization algorithm that was developed by researchers at Chalmers University of Technology.
Optimization of the robot's movements reduces acceleration and deceleration, as well as the time the robot is at a standstill since being at a standstill also consumes energy.
"We simply let the robot move slower instead of waiting for other robots and machines to catch up before carrying out the ...
2015-08-24
The public sector has long served as an equalizer in American society, a place where minority workers could find stable employment that offered advancement and a reliable path to a middle-class life.
But the Great Recession wiped out many of those jobs, as tax revenues declined and anti-government sentiment added to a contraction that continued long after the Great Recession ended in 2008. Those job cuts disproportionately hurt African-American workers and increased racial disparity in the public sector, a new study by University of Washington sociologist Jennifer Laird ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] GPM sees rainfall in Tropical Depression Kilo nearing Johnston Island

