AI system reveals new insights into early language acquisition through the experience of a single child
2024-02-01
A new machine learning model – trained on video and audio recorded from the first-person perspective of one young child for over a year – has provided new insights into early language acquisition. Not only do the findings offer a valuable framework to understand how children learn words and concepts, but they could be critical in developing artificial intelligence (AI) systems that can learn language in more human-like ways. Beginning around 6 to 9 months of age, children begin acquiring their ...
Targeting treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
2024-02-01
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL FEB. 1, 2024, AT 2 P.M. ET) – New research from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations has identified a next-generation BTK degrader that could help overcome treatment resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and related blood cancers.
Their findings, published Feb. 2 in the journal Science, could offer a therapeutic option for CLL patients whose tumors become drug-resistant or are unresponsive to frontline treatment.
“This new compound not only inhibits the cellular molecule BTK, but goes further by taking aim at the target ...
Sustainable carbon removals limits identified, huge climate mitigation challenge revealed
2024-02-01
*Embargoed until 14:00 US Eastern / 19:00 UK GMT / 20:00 Europe CET – Thursday 1 February*
Governments and businesses are relying on dangerous amounts of future removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, instead of more rapidly reducing emissions and phasing out fossil fuels. This problem is partly due to an incomplete picture1 of the damaging consequences of carbon dioxide removal for people, food security and natural ecosystems, according to new research published in Science.
The paper finds that the carbon dioxide removal potential currently reported by the UN ...
Whole-brain projection patterns of single neurons in mouse hippocampus unveiled
2024-02-01
A study published in Science on Feb. 1 reported a comprehensive database of single-neuron projectomes consisting of over 10,000 mouse hippocampal neurons, thus revealing the spatial connectivity patterns of mouse hippocampal neurons at the mesoscopic level.
The study was conducted by teams from the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology (CEBSIT), the Institute of Neuroscience of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the HUST-Suzhou Institute for Brainsmatics, Hainan University, the Kunming Institute of Zoology of CAS, Lingang Laboratory, and the Shanghai Center for ...
New study suggests culling animals who ‘don’t belong’ can be a flawed nature conservation practice
2024-02-01
New research published today in the journal Science has concluded that eradicating animals on the basis that they are not native in order to protect plant species, can be a flawed practice costing millions of dollars, and resulting in the slaughter of millions of healthy wild animals.
Introduced large herbivores, or megafauna, are claimed to have distinct and harmful ecological impacts, including damaging sensitive plants and habitats, reducing native plant diversity, and facilitating introduced plants. However, up to now these impacts have been studied without comparison to a proper ...
IU surgeon-scientist studying physiological effect of microorganisms in sinuses of chronic rhinosinusitis patients
2024-02-01
INDIANAPOLIS—An Indiana University School of Medicine surgeon-scientist is leading a multi-institutional grant investigating the role of the sinus microbiome in chronic rhinosinusitis, an inflammatory disease that causes the lining of the sinuses to swell. The research team will study biospecimens from human sinus surgery patients in the lab and examine how bacteria in the microbiome shape the disease process and might offer novel therapeutic strategies.
Vijay Ramakrishnan, MD, professor of otolaryngology—head ...
Stand Up to Cancer announces changes to scientific advisory committee
2024-02-01
LOS ANGELES – February 1, 2024 – Stand Up To Cancer® (SU2C) today announced changes to its Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC), which oversees SU2C’s scientific research.
Composed of cancer research leaders from academic, government, industry, and advocacy fields, SU2C’s SAC sets direction for research initiatives, reviews proposals for new grant awards, and conducts rigorous oversight of all active grants in the SU2C research portfolio in collaboration with SU2C’s president and CEO Julian Adams, Ph.D.
World renowned cancer researcher and Nobel laureate Phillip A. Sharp, Ph.D., who has chaired the SAC since SU2C launched in ...
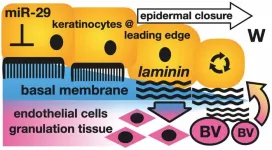
Small RNAs take on the big task of helping skin wounds heal better and faster with minimal scarring
2024-02-01
Philadelphia, February 1, 2024 – New findings in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, report that a class of small RNAs (microRNAs), microRNA-29, can restore normal skin structure rather than producing a wound closure by a connective tissue (scar). Any improvement of normal skin repair would benefit many patients affected by large-area or deep wounds prone to dysfunctional scarring.
Because the burden of non-healing wounds is so significant, it is sometimes called a “silent pandemic.” Worldwide, costs associated with wound care are expected to ...
Rural placements for medical students feed ‘pipeline’ for new family docs
2024-02-01
EDMONTON — New research shows an innovative education program is helping to address Alberta’s rural doctor shortage by making it more likely medical students will set up a rural family practice after graduation.
The University of Alberta was one of the first medical schools in Canada to set up its Rural Integrated Community Clerkship program back in 2007. It sends up to 25 third-year students for 10-month intensive work experiences with a single or small number of teaching physicians.
Instead of rotating to a new specialty placement every four to six weeks as in an urban ...
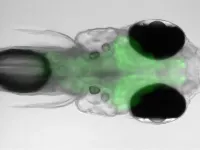
Zebrafish navigate to find their comfortable temperature
2024-02-01
All animals need to regulate their body temperature and cannot survive for long if it gets too high or too low. Warm-blooded organisms like humans have various ways to do this. They release heat by sweating or expanding the blood vessels in their skin, while shivering or burning fat in their brown adipose tissue has the opposite effect.
Cold-blooded animals such as the zebrafish, by contrast, cannot do any of these, so they have a different strategy. They look for places nearby that are at their “comfortable temperature,” just like how we might go out into the sun when we feel chilly or seek out some shade once it gets too ...
Buck scientists discover a potential way to repair synapses damaged in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-02-01
While newly approved drugs for Alzheimer’s show some promise for slowing the memory-robbing disease, the current treatments fall far short of being effective at regaining memory. What is needed are more treatment options targeted to restore memory, said Buck Assistant Professor Tara Tracy, PhD, the senior author of a study that proposes an alternate strategy for reversing the memory problems that accompany Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias.
Since most current research on potential treatments for Alzheimer’s focuses on reducing the toxic proteins, such as tau and amyloid beta, that accumulate in ...
Researchers identify critical pathway responsible for melanoma drug resistance
2024-02-01
(Boston)—One of the major challenges in cancer research and clinical care is understanding the molecular basis for therapeutic resistance as a major cause of long term treatment failures. In cases of melanoma, the main targeted therapeutic strategy is directed against the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Unfortunately, in the vast majority of these patients, resistance to MAPK inhibitor therapies develops within one year of treatment.
In a new study from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, ...
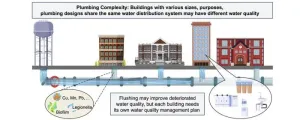
Pandemic lockdowns and water quality: a revealing study on building usage
2024-02-01
During the COVID-19 pandemic, lower occupancy in buildings led to reduced water use, raising concerns about water quality due to stagnation. Government warnings highlighted increased risks of chemical and microbiological contamination in water systems. Studies showed that reduced usage and stagnation could elevate heavy metal levels and decrease disinfectant effectiveness, affecting microbial growth. To address this, regular fixture flushing was recommended, which temporarily improved water quality but also revealed the complexities of managing building water systems effectively.
In a recent study (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2023.100314) ...
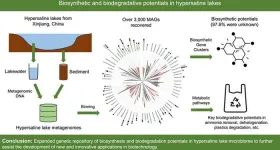
Exploring the unseen: microbial wonders in earth's saltiest waters
2024-02-01
The study delves into hypersaline lakes in Xinjiang, China, exploring the genetic and metabolic diversity of microbial communities termed "microbial dark matters". Hypersaline lake ecosystems, characterized by extreme salinity, harbor unique microorganisms with largely unexplored biosynthesis and biodegradation capabilities. The research seeks to uncover novel biological compounds and pathways, potentially revolutionizing biotechnology, medicine, and environmental remediation by tapping into the untapped potential of these extremophiles.
A recent study (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2023.100359) published ...
As cancer therapies improve, more patients with rectal cancer forego surgery
2024-02-01
While surgery to remove rectal cancer can be necessary and lifesaving, it can sometimes come with significant drawbacks, like loss of bowel control. According to a study led by Wilmot Cancer Institute researchers, patients with rectal cancer who respond well to radiation and chemotherapy are increasingly foregoing surgery and opting for a watch-and-wait approach.
The study, published in JAMA Oncology, shows that the number of patients opting out of surgery rose nearly 10 percent between 2006 and 2020. These data reflect a shift toward what ...
Stanford Medicine-led study shows why women are at greater risk of autoimmune disease
2024-02-01
Somewhere between 24 and 50 million Americans have an autoimmune disease, a condition in which the immune system attacks our own tissues. As many as 4 out of 5 of those people are women.
Rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and scleroderma are examples of autoimmune disorders marked by lopsided female-to-male ratios. The ratio for lupus is 9 to 1; for Sjogren’s syndrome, it’s 19 to 1.
Stanford Medicine scientists and their colleagues have traced this disparity to the most fundamental feature differentiating ...
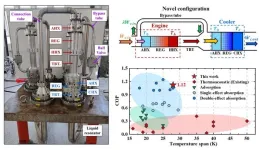
Researchers develop highly efficient heat-driven thermoacoustic refrigerator
2024-02-01
Researchers led by Prof. LUO Ercang from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (TIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and their collaborators have developed an innovative heat-driven thermoacoustic refrigerator (HDTR) with a novel bypass configuration that significantly improves the efficiency of this technology.
The study was published in Cell Reports Physical Science on Feb. 1.
HDTR is recognized as a new, promising cooling technology with many advantages. For example, it has no moving parts, uses eco-friendly substances (e.g., helium and nitrogen), and is highly reliable. However, its relatively low efficiency ...
Animals: Small, long-nosed dogs live the longest
2024-02-01
Small long-nosed (or dolichocephalic) dog breeds such as Whippets have the highest life expectancies in the UK, whilst male dogs from medium-sized flat-faced (or brachycephalic) breeds such as English Bulldogs have the lowest. The results, published in Scientific Reports, have been calculated from data on over 580,000 individual dogs from over 150 different breeds, and could help to identify those dogs most at risk of an early death.
Kirsten McMillan and colleagues assembled a database of 584,734 individual dogs using data from 18 different UK sources, including breed registries, vets, pet insurance companies, animal welfare ...
Physical activity and cognitive decline among older adults
2024-02-01
About The Study: Physical activity was associated with better late-life cognition, but the association was weak in this systematic review and meta-analysis including 104 studies with 341,000 participants. However, even a weak association is important from a population health perspective.
Authors: Paula Iso-Markku, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Helsinki, Finland is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54285)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Cerebral cortical surface structure and neural activation pattern among adolescent football players
2024-02-01
About The Study: In this study of 205 adolescent football players and 70 noncontact control athletes, there was evidence of discernible structural and physiological differences in the brains of adolescent football players compared with their noncontact controls. Many of the affected brain regions were associated with mental health well-being.
Authors: Keisuke Kawata, Ph.D., of Indiana University in Bloomington, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54235)
Editor’s ...
BU professor to serve on the National Academies’ New Voices in Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Program
2024-02-01
(Boston)—Sabrina A. Assoumou, MD, MPH, the inaugural Louis W. Sullivan, MD, Professor of Medicine, and an associate professor of medicine at Boston University Chobanian and Avedisian School of Medicine, has been selected to serve in the 2024-2026 cohort of New Voices in Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine at the National Academies. Participants are selected in recognition of outstanding achievements and the program provides an opportunity to identify and address pressing concerns for the nation.
New Voices ...
The ShAPE of buildings to come: Scrap aluminum transforms recycling life cycle
2024-02-01
RICHLAND, Wash.—The circular economy just closed the loop on scrap aluminum, thanks to a new patent-pending technology developed at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. That twisted aluminum mesh, those banged up bicycle frames, and the used car parts now languishing in junk yards could gain new life as building structures such as door and window frames, facades, lighting, decorative features and a myriad of other uses—all while conserving nearly all the energy required to manufacture new aluminum products.
It’s no secret that strong, yet light-weight aluminum parts are being ...
A positive spin—electrospinning and electrospraying synergism for the nanomaterials industry
2024-02-01
Combining these two twins-tech, electrospinning and electrospraying, to fabricate novel nanomaterials is an urgent area of research for materials scientists and biomedical engineers, according to a new paper by Professor Hu Jinlian of City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) published in Matter, a highly respected monthly journal encompassing materials science, from nano to macro, and from fundamentals to application.
The electrospinning and electrospraying synergism (ESS) can positively impact diverse sectors, from bioengineering and ...
cfDNA sequencing enhances non-invasive early detection of gestational diabetes
2024-02-01
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a prevalent pregnancy complication posing significant health risks to both mothers and their newborns. Early detection and treatment of GDM are crucial to prevent adverse outcomes. Current screening methods, like glucose tolerance tests, are in after 24 weeks of pregnancy and have limitations in patient compliance and accuracy.
A new study led by Lijian Zhao, Pei Sun, Hui Huang, Nan Li at BGI Genomics in collaboration with the Beijing Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, recently published on Briefings in Bioinformatics ...
Promising heart drugs ID'd by cutting-edge combo of machine learning, human learning
2024-02-01
University of Virginia scientists have developed a new approach to machine learning – a form of artificial intelligence – to identify drugs that help minimize harmful scarring after a heart attack or other injuries.
The new machine-learning tool has already found a promising candidate to help prevent harmful heart scarring in a way distinct from previous drugs. The UVA researchers say their cutting-edge computer model has the potential to predict and explain the effects of drugs for other diseases as well.
“Many common diseases such as heart disease, ...
[1] ... [1397]
[1398]
[1399]
[1400]
[1401]
[1402]
[1403]
[1404]
1405
[1406]
[1407]
[1408]
[1409]
[1410]
[1411]
[1412]
[1413]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.