Blood stem cells unlock clues for helping sepsis patients fight recurring infections
2024-04-11
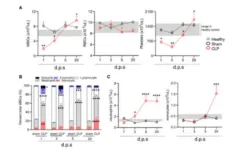
Severe sepsis from bacterial or viral infections can be life-threatening and even people recovering from severe sepsis may experience long-lasting effects on the immune system, making them more susceptible to recurrent infections. The causes for this sepsis-induced immune suppression are not well understood and lack an effective treatment. To better understand the cause, Katherine MacNamara and colleagues from Albany Medical College, USA, analyzed the blood stem cells of mice with prior sepsis and their results were recently published in the journal Stem Cell Reports.
During ...
Climate: Increased threat to coastlines from concurrent heatwaves and sea level rises
2024-04-11
Concurrent occurrences of heatwaves and extreme short-term sea level rises at the same coastal locations significantly increased between 1998 and 2017 when compared to the preceding twenty years, reports a study published in Communications Earth & Environment. The study also suggests that these events may be five times more likely to occur between 2025 and 2049 under a modelled high emissions scenario.
A so-called ‘concurrent heatwave and extreme sea level’ (CHWESL) event is when a heatwave and an extreme short-term sea level rise occur at the same coastal location over the same time period. Although they ...
Second primary breast cancer in young breast cancer survivors
2024-04-11
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that young breast cancer survivors without a germline pathogenic variant have a low risk of developing a second primary breast cancer in the first 10 years after diagnosis. Findings from germline genetic testing may inform treatment decision-making and follow-up care considerations in this population.
Authors: Kristen D. Brantley, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Physician empathy and chronic pain outcomes
2024-04-11
About The Study: In this study that included 1,470 adults with chronic low back pain, physician empathy was associated with better outcomes over 12 months. Greater efforts to cultivate and improve physician empathy appear warranted.
Authors: John C. Licciardone, D.O., M.S., M.B.A., of the University of North Texas Health Science Center at Fort Worth, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.6026)
Editor’s ...
Tropical coral-infecting parasites discovered in cold marine ecosystems
2024-04-11
Parasites thought only to infect tropical coral reefs have been discovered in a large variety of creatures in cold marine ecosystems along the Northeast Pacific, according to new research from University of British Columbia botanists.
The finding, published today in Current Biology, greatly expands the range of corallicolids, suggesting the parasites infect a range of organisms related to coral, like sea anemones and other cold-water marine invertebrates, around the world.
“This highlights significant blind spots in our strategies designed to sample microbial biodiversity,” says University of British Columbia biodiversity researcher Dr. Patrick Keeling, senior author on the ...
Successful murine model of dermatomyositis reveals underlying immune system involvement
2024-04-11
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have developed a murine model for a highly progressive disease called “anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis”, providing insights into underlying biological mechanisms and aiding treatment
Tokyo, Japan – Some diseases involve autoimmune reactions, when the body begins to attack its own cells and proteins. The biological mechanisms underlying these diseases are often unknown, making treatment challenging. Now, a group at TMDU has created a murine model for a disease ...
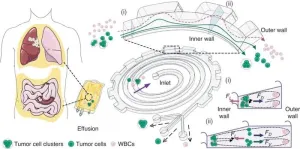
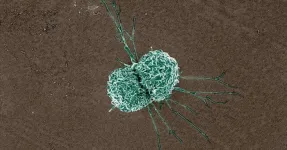
Next-gen lab chip transforms cancer detection: triple-threat cell sorting unveiled
2024-04-11
Researchers have unveiled a microfluidic device that significantly improves the separation of tumor cells and clusters from malignant effusions. This novel technology promises to advance the diagnosis and treatment monitoring of cancer by enabling the high-throughput, continuous-flow ternary separation of single tumor cells, tumor cell clusters, and white blood cells (WBCs) from clinical pleural or abdominal effusions.
Understanding the nature of malignant effusions, teeming with tumor cells and clusters, is critical in comprehending the breadth of cancer's impact. The significant role of tumor clusters, with their heightened potential ...
NCCN 2024 Annual Conference shares cancer care updates for practical, immediate use in practice
2024-04-11
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 11, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—hosted more than 1,700 oncology professionals during the NCCN 2024 Annual Conference on April 5-7. The yearly meeting includes opportunities for care providers to interact with world-renowned specialists on the latest evidence-based expert consensus recommendations for delivering high quality, patient-centered cancer care. Sessions focused on practical applications for improving care at every level, including clinical and administrative ...
Genetic underpinnings of environmental stress identified in model plant
2024-04-11
Plants can be temperamental. Even weeds along the side of highways or pushing their way up in the cracks of concrete sidewalks can get stressed out by dehydration, cold, excess salt and more. Researchers at Hiroshima University have identified 14 genes that thale cress — a plant commonly used in genetic investigations since its genome is well documented — express more when responding to five specific stressors, as well as eight genes that the plant suppresses.
They published their results on March 22 in Frontiers in Plant Science.
“Abiotic stresses — as opposed to biotic stresses like pests or disease — such as drought, salinity and cold negatively ...
This outdated diabetes drug still has something to offer
2024-04-11
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are a class of drug that can be used to treat type 2 diabetes by reversing insulin resistance, one of the main hallmarks of the disease. While TZDs were extremely popular in the 1990’s and early 2000’s, they have fallen out of use among physicians in recent decades because they were discovered to cause unwanted side effects, including weight gain and excess fluid accumulation in body tissues.
Now, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine are ...
Developing best practices for human-AI collaboration in engineering design
2024-04-11
As artificial intelligence is inevitably woven into the workplace, teams of humans will increasingly collaborate with robots on complex design problems, such as those in the auto, aviation, and space industries.
“Right now, design is mainly done by humans, and it’s based on their expertise and intuitive decision-making, which is learned over time,” says A. Emrah Bayrak, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering and mechanics in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science. “Usually, ...
Novel CT exam reduces need for invasive artery treatment
2024-04-11
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study showed that a non-invasive imaging test can help identify patients with coronary artery blockage or narrowing who need a revascularization procedure. The findings were published as a Special Report in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Doctors use coronary CT angiography (CTA) to diagnose narrowed or blocked arteries in the heart. A CTA exam receives a score from mild (0-1) to moderate (2-3) to severe (4-5). Patients ...
ERC Advanced Grant: 2.5 million euros for Tobias Brixner
2024-04-11
Many people are familiar with the principle of electronic excitation from their physics lessons: electrons in atoms or molecules absorb energy, typically from light, and rise to a higher energy level. This can have various consequences – in photovoltaic technology, the phenomenon ensures that electricity can be generated from sunlight.
Measuring electronic excitation according to scientific standards and investigating how excited electrons influence each other is a real challenge: “Electronic excitation and the subsequent processes take place extremely quickly, many things happen simultaneously“, explains Tobias Brixner, Chair of Physical Chemistry ...
Proud seafarers have strong doubts about the safety of autonomous ships
2024-04-11
The maritime profession is among the world’s oldest professions, and today’s shipping is based on long and proud traditions. Professional pride and commitment are often deeply ingrained in seafarers, and for many, the job is more of a way of life. New technologies will bring about major changes in the work of bridge officers, who have the ultimate responsibility on board Norwegian vessels.
Strong doubts about safety
“Bridge officers rely on automated systems that are already found on board, such as advanced autopilot systems. However, there is strong scepticism, almost mistrust, that increased automation and autonomous ...
People who use willpower alone to achieve goals, resist temptation, deemed more trustworthy
2024-04-11
People who use willpower to overcome temptations and achieve their goals are perceived as more trustworthy than those who use strategies that involve external incentives or deterrents – such as swear jars or internet-blocking apps – according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“The knowledge that people can use external commitment strategies to overcome self-control problems has existed in some form for thousands of years. Since at least the time of Homer and Odysseus, the focus has primarily been on the efficacy of these strategies for the person choosing to engage ...
New study shows effect of socio-economic factors—housing, food, neighborhood—to predict diabetic patients’ risk of heart failure
2024-04-11
CLEVELAND—A recent study by Case Western Reserve University used national data from U.S. military veterans with diabetes to validate and modify a widely accepted model used to predict the risk of heart failure in diabetic patients.
The model, called the WATCH-DM score, is used to predict the likelihood of heart failure in diabetes patients within five years.
But because it overlooks the influence of social determinants of health‚ such as housing, food and a patient’s neighborhood, the researchers used a social deprivation index (SDI), a multi-component summary score, to adjust the WATCH-DM score.
The SDI, introduced by the Robert ...
Mapped: 33 new big game migrations across American West
2024-04-11
RESTON, Va. — A new set of maps that document the movements of ungulates was published today in the fourth volume of the Ungulate Migrations of the Western United States. The maps in this collaborative U.S. Geological Survey report series reveal the migration routes and critical ranges used by ungulates, or hooved mammals, in the western U.S., furthering scientists’ understanding of the geography of big game migrations.
The new volume, “Ungulate Migrations of the Western United States: Volume 4,” documents 33 mule deer, ...
Can we crack the code of cartilage?
2024-04-11
Can Jos Malda crack the code of cartilage?
In our aging society, healing joint problems is becoming increasingly important. To do this, cartilage damage must become repairable. But so far it has proven impossible to recreate the intricate internal structure of cartilage. Professor Jos Malda has now received an ERC Advanced grant of €2.5 million to crack that code.
Bringing biology and technology together
Throughout his career, Jos Malda has been concerned with the interface between biology and technology. It took him from studying Bioprocess Engineering in Wageningen to ...
Moments of clarity in the fog of dementia
2024-04-11
A recent Mayo Clinic study published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association investigated lucid episodes in people living with later stages of dementia, providing insights into how these occurrences reveal themselves.
The findings showed that 75% of people having lucid episodes were reported to have Alzheimer’s Disease as opposed to other forms of dementia.
Researchers define lucid episodes as unexpected, spontaneous, meaningful and relevant communication from a ...
Heart transplant recipient discovers a calling for advocacy, support for others
2024-04-11
11 April, Prague, Czech Republic—Glen Kelley’s journey as a heart transplant recipient came full circle today in Prague, as he addressed attendees of the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT), including members of his own care teams.
As a high school senior outside of Peoria, Illinois, Kelley was diagnosed with stage-4 Hodgkin’s lymphoma and underwent eight months of chemotherapy and radiation. After 10 months in remission, the ...
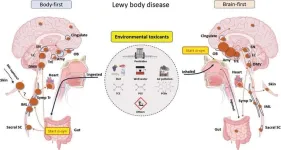
On World Parkinson’s Day, a new theory emerges on the disease’s origins and spread
2024-04-11
The nose or the gut? For the past two decades, the scientific community has debated the wellspring of the toxic proteins at the source of Parkinson’s disease. In 2003, a German pathologist, Heiko Braak, MD, first proposed that the disease begins outside the brain. More recently, Per Borghammer, MD, with Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark, and his colleagues argue that the disease is the result of processes that start in either the brain’s smell center (brain-first) or the body’s intestinal tract (body-first).
A new hypothesis paper appearing in the Journal of Parkinson’s ...
ERC wants to see what shapes the stories AI tells us
2024-04-11
Professor Jill Walker Rettberg, Co-Director of the Centre for Digital Narrative at the University of Bergen, is awarded an ERC Advanced Grant for the project AI STORIES. The grant consists of 2.5 million Euro over 5 years. This is Rettberg's second ERC Grant.
“The AI STORIES project builds on the premise that storytelling is central to human culture, with narratives shaping our understanding of the world. We will study artificial intelligence and how it creates new narratives,” says Rettberg.
Generative AI has been dubbed ...
New project explores warfare in animal societies
2024-04-11
A major new research project will investigate how and why groups of animals from the same species fight one another.
By focussing on warlike species – mongooses and termites – researchers aim to understand how evolution can lead to extreme aggression between groups, the consequences of this and the factors that can lead to peace.
The results will help to explain why violence between rival groups evolves in some species but not others, or between some groups and not others – with implications for our understanding of human evolution.
The research team, led by Professor ...
Mirta Galesic awarded ERC Advanced Grant
2024-04-11
[Vienna, April 11, 2024] – The European Research Council (ERC) has awarded an Advanced Grant to Mirta Galesic, a resident scientist at the Complexity Science Hub (CSH), to study the intricate workings of collective adaptation. The project aims to provide insights into why collectives – from families to entire societies – can be stuck in deadlocks about important problems, such as resolving long-standing political conflicts; or why they sometimes appear incapable of finding seemingly obvious solutions, such ...
Twinkle twinkle baby star, 'sneezes' tell us how you are
2024-04-11
Fukuoka, Japan—Kyushu University researchers have shed new light into a critical question on how baby stars develop. Using the ALMA radio telescope in Chile, the team found that in its infancy, the protostellar disk that surrounds a baby star discharges plumes of dust, gas, and electromagnetic energy. These 'sneezes,' as the researchers describe them, release the magnetic flux within the protostellar disk, and may be a vital part of star formation. Their findings were published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Stars, including our Sun, all develop from what are called stellar nurseries, large ...
[1] ... [26]
[27]
[28]
[29]
[30]
[31]
[32]
[33]
34
[35]
[36]
[37]
[38]
[39]
[40]
[41]
[42]
... [7603]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.